Summary:
“Ode on a Grecian Urn” is one of John Keats’ most famous odes, written in 1819. The poem explores the relationship between art and life, focusing on an ancient Grecian urn that tells a silent yet eternal story through its images. Keats marvels at the figures on the urn—lovers, musicians, and pastoral scenes—who are forever frozen in time, untouched by decay or sorrow. The poem contrasts the permanence of art with the fleeting nature of human existence. It concludes with the famous philosophical statement: “Beauty is truth, truth beauty,” emphasizing that art captures an idealized reality that remains unchanged across generations.
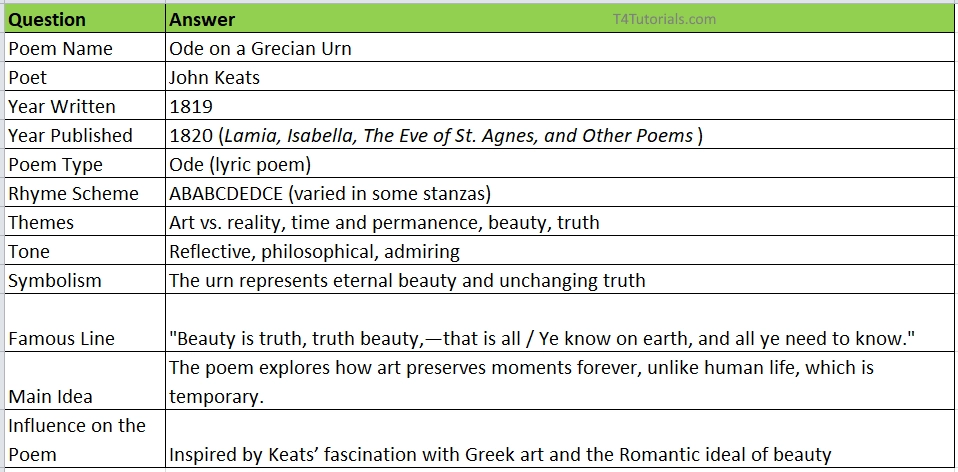
| Question | Answer |
| Poem Name | Ode on a Grecian Urn |
| Poet | John Keats |
| Year Written | 1819 |
| Year Published | 1820 (Lamia, Isabella, The Eve of St. Agnes, and Other Poems) |
| Poem Type | Ode (lyric poem) |
| Rhyme Scheme | ABABCDEDCE (varied in some stanzas) |
| Themes | Art vs. reality, time and permanence, beauty, truth |
| Tone | Reflective, philosophical, admiring |
| Symbolism | The urn represents eternal beauty and unchanging truth |
| Famous Line | “Beauty is truth, truth beauty,—that is all / Ye know on earth, and all ye need to know.” |
| Main Idea | The poem explores how art preserves moments forever, unlike human life, which is temporary. |
| Influence on the Poem | Inspired by Keats’ fascination with Greek art and the Romantic ideal of beauty |
20
Score: 0
Attempted: 0/20
Subscribe
Score: 0
Attempted: 0/20
Subscribe
MCQs & Summary of Some Famous Poems of John Keats
- Ode to a Nightingale MCQs & Summary
- Ode on a Grecian Urn MCQs & Summary
- Ode to Autumn MCQs & Summary
- Ode on Melancholy MCQs & Summary
- Ode to Psyche MCQs & Summary
- Ode on Indolence MCQs & Summary
- La Belle Dame sans Merci MCQs & Summary
- Bright Star, would I were steadfast as thou art MCQs & Summary
- When I Have Fears That I May Cease to Be MCQs & Summary
- The Eve of St. Agnes MCQs & Summary
- Lamia by John Keats MCQs & Summary
- Hyperion by John Keats MCQs & Summary
- Isabella, or the Pot of Basil MCQs & Summary
- On First Looking into Chapman’s Homer Summary
- Endymion Summary
Famous English Authors MCQs
- William Wordsworth MCQs
- William Shakespeare MCQs
- Robert Browning MCQs
- W B Yeats MCQs
- Edmund Spenser MCQs
- Chaucer MCQs
- John Milton MCQs
- S T Coleridge MCQs
- Lord Byron MCQs
- PB Shelley MCQs
- John Dryden MCQs
- John Keats MCQs
- Charles Dicken MCQs
- Alfred Lord Tennyson MCQs
- Charles Lamb MCQs
- D.H Lawrence MCQs
- Thomas Hardy MCQs
- Matthew Arnold MCQs
- John Galsworthy MCQs
- George Bernard Shaw MCQs
- T.S Eliot MCQs
- Ben Jonson MCQs
- Francis Bacon MCQs
- Alexander Pope MCQs
- Oliver Goldsmith MCQs
- Joseph Addison MCQs
- Dr Samuel Johnson MCQs
- Henry Fielding MCQs
- Sir Walter Scott MCQs
- Jane Austen MCQs
- Dr. Samuel Johnson MCQs
- English Comedy MCQs (Oliver Goldsmith)
- Alexander Pope MCQs (Neo-Classical Age of English Poetry)
- Daniel Defoe MCQs
- Dr. Jonathan Swift MCQs
- Richard Steele MCQs
- English Drama MCQs
- Elizabethan Drama MCQs [14th to 17th century]
- Elizabethan Prose MCQs
More English Literature MCQs
- English Poetry MCQs
- History of English Literature MCQs
- Sentimental Novels MCQs
- Sentimental Poetry MCQs
- Legends Of English Literature MCQs
- English Literature Quiz
- English Literature Important Multiple Choice Questions Answers
- Sons And Lovers by D H Lawrence MCQs
- The Waste Land, A Poem by T. S. Eliot MCQs
- Drama Origin MCQs
- History of the Renaissance Period MCQs
- English Pros MCQs
- Non-Dramtic Poets Of The Elizabethan Age MCQs
- The Cavalier Poets of 17th-century MCQs
- Metaphysical Poets of 17th century MCQs
- Renaissance Period of 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries MCQs
- Puritan Poet MCQs
- Restoration Comedy by William Congreve & Wycherley MCQs
- Satire MCQs – Renaissance Period by John Dryden
- English Essayists MCQs
- Romantic Period of Romantic Poets MCQs
- English language MCQs
- English Humour MCQs [American Literature]
- Early Writers of American Literature MCQs
- History of American Literature MCQs
- American Prose MCQs [English Realism ]
- American English Critics
- New Englanders Authors MCQs
- MCQs on American Literature After Independence
- American Playwrights MCQs
- New American Poetry MCQs
- British English Critics MCQs
- Ancient English literature MCQs
- Important English Literature MCQs for Public Service Commission
- English Literature Repeated Important MCQs
- CSS English Literature MCQs
- History of Early Period MCQs
- The Anglo-Saxon period MCQs
- The Age of Chaucer in the Early Period MCQs
- The Anglo-Norman Period of French Writers MCQs
- Metrical Romances MCQ (Anglo-Saxon Period)
- Revival of Learning MCQs (1400-1550)
- Applied Linguistics MCQs
- Language Change MCQs