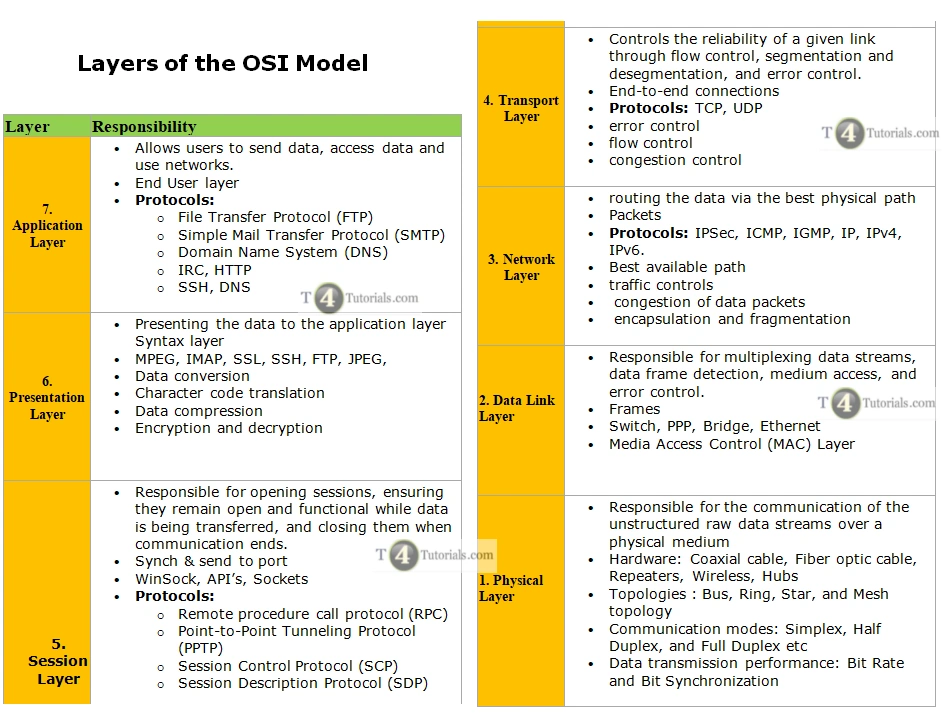
| Layer |
Responsibility |
| 7. Application Layer |
- Allows users to send data, access data, and use networks.
- End User layer
- Protocols:
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- IRC, HTTP
- SSH, DNS
|
| 6. Presentation Layer |
- Presenting the data to the application layer Syntax layer
- MPEG, IMAP, SSL, SSH, FTP, JPEG,
- Data conversion
- Character code translation
- Data compression
- Encryption and decryption
|
| 5. Session Layer |
- Responsible for opening sessions, ensuring they remain open and functional while data is being transferred, and closing them when communication ends.
- Synch & send to port
- WinSock, API’s, Sockets
- Protocols:
- Remote procedure call protocol (RPC)
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
- Session Control Protocol (SCP)
- Session Description Protocol (SDP)
|
| 4. Transport Layer |
- Controls the reliability of a given link through flow control, segmentation and desegmentation, and error control.
- End-to-end connections
- Protocols: TCP, UDP
- error control
- flow control
- congestion control
|
| 3. Network Layer |
- routing the data via the best physical path
- Packets
- Protocols: IPSec, ICMP, IGMP, IP, IPv4, IPv6.
- Best available path
- traffic controls
- congestion of data packets
- encapsulation and fragmentation
|
| 2. Data Link Layer
|
- Responsible for multiplexing data streams, data frame detection, medium access, and error control.
- Frames
- Switch, PPP, Bridge, Ethernet
- Media Access Control (MAC) Layer
|
| 1. Physical Layer
|
- Responsible for the communication of the unstructured raw data streams over a physical medium
- Hardware: Coaxial cable, Fiber optic cable, Repeaters, Wireless, Hubs
- Topologies: Bus, Ring, Star, and Mesh topology
- Communication modes: Simplex, Half Duplex, Full Duplex, etc
- Data transmission performance: Bit Rate and Bit Synchronization
|