30
Score: 0
Attempted: 0/30
Subscribe
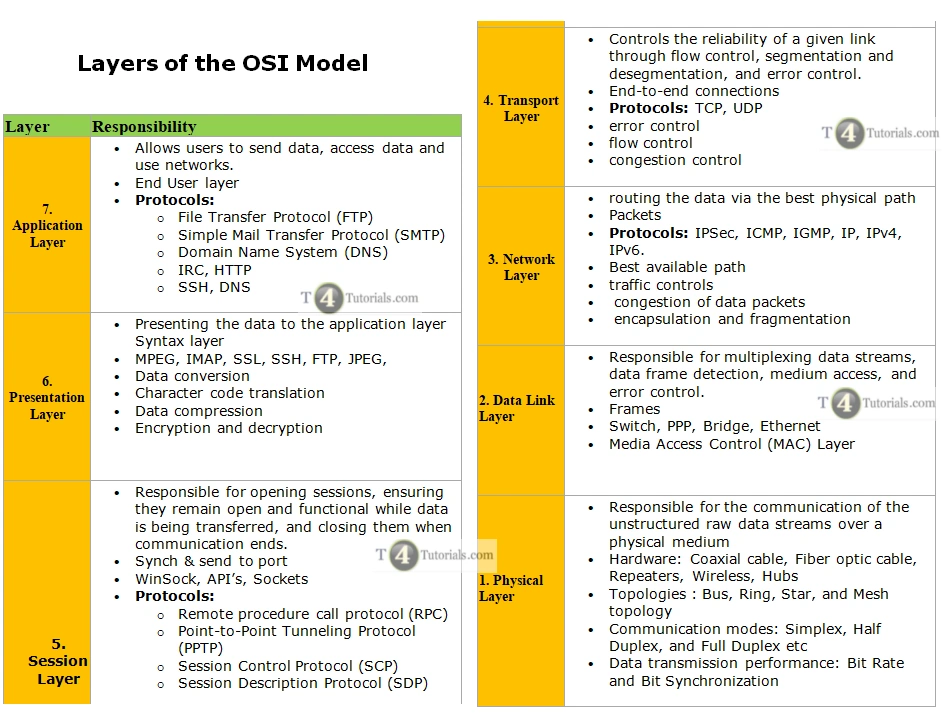
Layers of the OSI Model
| Layer | Responsibility |
| 7. Application Layer |
|
| 6. Presentation Layer |
|
| 5. Session Layer |
|
| 4. Transport Layer |
|
| 3. Network Layer |
|
| 2. Data Link Layer |
|
| 1. Physical Layer |
|