Comparison of Normal Forms 1NF vs 2NF vs 3NF vs BCNF in database systems.
Let’s see the difference between Normal Forms
1NF vs
2NF vs
3NF vs BCNF in database tables.
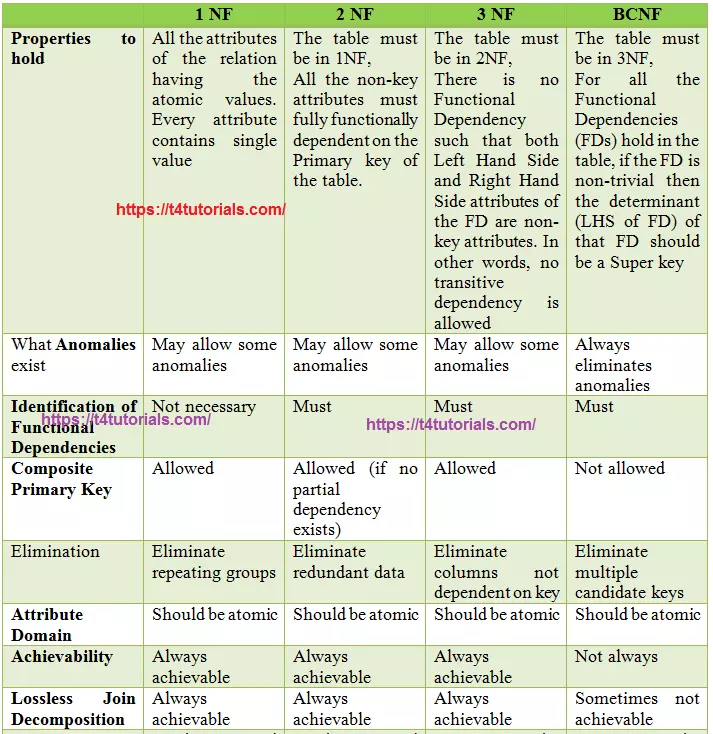
Properties to hold
1NF: All the attributes of the relation having the atomic values. Every attribute contains a single value
2NF: the table must be in 1NF, All the non-key attributes must fully functionally dependent on the Primary key of the table.
3NF: The table must be in 2NF. There is no Functional Dependency such that both Left-Hand Side and Right Hand Side attributes of the FD are non-key attributes. In other words, no transitive dependency is allowed.
3.5NF: The table must be in 3NF, For all the Functional Dependencies (FDs) hold in the table, if the FD is non-trivial then the determinant (LHS of FD) of that FD should be a Super key.
What Anomalies exist?
1NF: May allow some anomalies.
2NF: May allow some anomalies.
3NF: May allow some anomalies.
3.5NF: Always eliminates anomalies
Identification of Functional Dependencies
1NF: Not Compulsory.
2NF: Compulsory.
3NF: Compulsory.
3.5NF: Compulsory.
Composite Primary Key
1NF: Allowed.
2NF: Allowed (if no partial dependency exists).
3NF: Allowed.
3.5NF: Not Allowed.
Elimination
1NF: Elimination of repeating groups.
2NF: Elimination of redundant data.
3NF: Elimination of the columns not dependent on the key.
3.5NF: Elimination of multiple candidate keys.
Attribute Domain
1NF: Should be atomic.
2NF: Should be atomic.
3NF: Should be atomic.
3.5NF: Should be atomic.
Achievability
1NF: Always achievable.
2NF: Always achievable.
3NF: Always achievable.
3.5NF: Not Always achievable.
Lossless Join Decomposition
1NF: Always achievable.
2NF: Always achievable.
3NF: Always achievable.
3.5NF: Not Always. Sometimes not achievable.
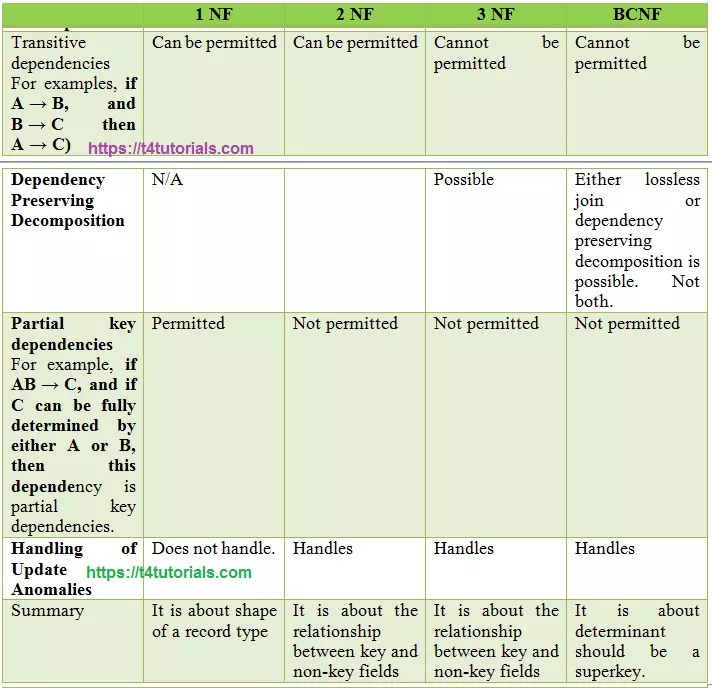
Transitive dependencies
For example, if A determines B, and B determines C then A determines C).
1NF: Can be permitted.
2NF: Can be permitted.
3NF: Cannot be permitted.
3.5NF: Cannot be permitted.
Dependency Preserving Decomposition
1NF: N/A.
2NF:
3NF: Possible.
3.5NF: Either lossless join or dependency preserving decomposition is possible. Not both.
Partial key dependencies
For example, if AB ? C, and if C can be fully determined by either A or B, then this dependency is partial key dependencies.
1NF: Permitted.
2NF: Not Permitted.
3NF: Not Permitted.
3.5NF: Not Permitted.
Handling of Update Anomalies
1NF: Does not handle.
2NF: Handles.
3NF: Handles.
3.5NF: Handles.
Summary
1NF: 1NF is about the shape of a record type.
2NF: 2NF is about the relationship between key and non-key fields.
3NF: 3NF is about the relationship between key and non-key fields.
3.5NF: 3.5NF is about determinant should be a superkey.



