What is a spiral model?
The spiral model is a combination of waterfall, incremental, iterative and prototype model. It is mostly used for big projects where continuous changes are required.Phases of the spiral model
- Planning
- Risk analysis
- Engineering and Construction
- Evaluation
| Phase | Activities | Deliverable |
| Planning | ≡ Requirement gathering ≡ Requirement analysis ≡ Requirement specification ≡ Requirement negotiation ≡ Requirement modeling ≡ Requirement Management | Software Requirement Specification document (SRS) |
| Risk Analysis | ≡ Risk identification ≡ Prioritization of risk ≡ Risk reduction (Mitigation) ≡ Risk impact reduction ≡ Risk monitoring | Risk detailed document |
| Engineering | ≡ Development ≡ Testing | ≡ Code ≡ Test cases document, Test report document ≡ Fault report document |
| Evaluation | ≡ Initial Validation by stakeholders ≡ Final Validation by customer | Evaluation report document |
What are the advantages of the spiral model?
≡ Ensure risk reduction ≡ Useful for large projects ≡ Changes can be handled in the next iteration/loop. ≡ Most suitable for real-time systemsWhat are the disadvantages of the spiral model?
≡ Expert required for risk reduction ≡ More costly ≡ Not suitable for small projects ≡ Project duration can be infinite because of its spiral behavior. ≡ Project cost can be infinite because of its spiral behavior ≡ Documentation can be very large arial, helvetica, sans-serif;”>≡ Not suitable for the projects with low riskWhen to use the spiral model?
≡ When the risk is medium or high ≡ When software is to be used in a very sensitive and dangerous environment. ≡ For real-time systems ≡ For large projects ≡ When requirements are not clear ≡ When changes in the software can be expected at any time.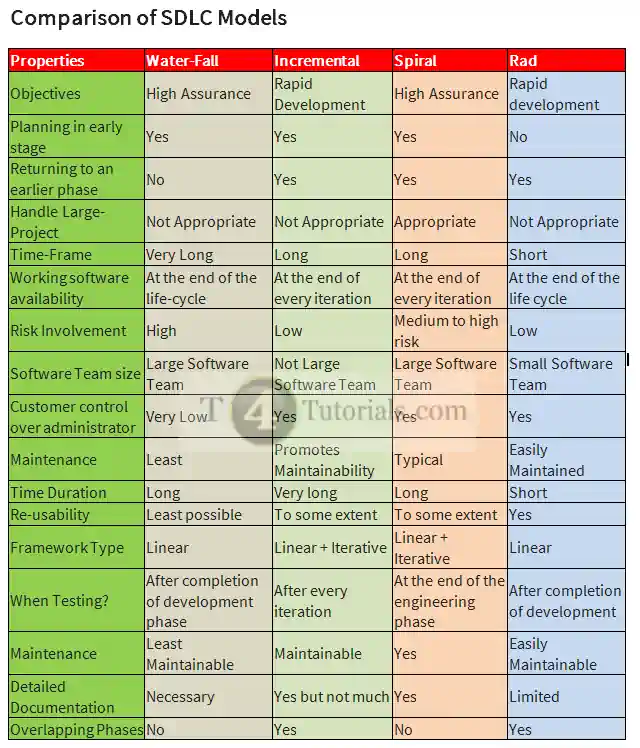
Comparison of spiral model and waterfall model
| Properties | Spiral | Waterfall |
| Objectives | High Assurance | High Assurance |
| Planning in early stage | Yes | Yes |
| Returning to an earlier phase | Yes | No |
| Handle Large-Project | Appropriate | Not Appropriate |
| Time-Frame | Long | Very Long |
| Working software availability | At the end of every iteration | At the end of the life-cycle |
| Risk Involvement | Medium to high risk | High |
| Software Team size | Large Software Team | Large Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator | Yes | Very Low |
| Maintenance | Typical | Least |
| Time Duration | Long | Long |
| Re-usability | To some extent | Least possible |
| Framework Type | Linear + Iterative | Linear |
| When Testing? | At the end of the engineering phase | After completion of development phase |
| Maintenance | Yes | Least Maintainable |
| Detailed Documentation | Yes | Necessary |
| Overlapping Phases | No | No |
Comparison of spiral model and incremental model
| Properties | Spiral | Incremental |
| Objectives | High Assurance | Rapid Development |
| Planning in early stage | Yes | Yes |
| Returning to an earlier phase | Yes | Yes |
| Handle Large-Project | Appropriate | Not Appropriate |
| Time-Frame | Long | Long |
| Working software availability | At the end of every iteration | At the end of every iteration |
| Risk Involvement | Medium to high risk | Low |
| Software Team size | Large Software Team | Not Large Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator | Yes | Yes |
| Maintenance | Typical | Promotes Maintainability |
| Time Duration | Long | Very long |
| Re-usability | To some extent | To some extent |
| Framework Type | Linear + Iterative | Linear + Iterative |
| When Testing? | At the end of the engineering phase | After every iteration |
| Maintenance | Yes | Maintainable |
| Detailed Documentation | Yes | Yes but not much |
| Overlapping Phases | No | Yes |
Comparison of spiral model and RAD
| Properties | Spiral | Rad |
| Objectives | High Assurance | Rapid development |
| Planning in early stage | Yes | No |
| Returning to an earlier phase | Yes | Yes |
| Handle Large-Project | Appropriate | Not Appropriate |
| Time-Frame | Long | Short |
| Working software availability | At the end of every iteration | At the end of the life cycle |
| Risk Involvement | Medium to high risk | Low |
| Software Team size | Large Software Team | Small Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator | Yes | Yes |
| Maintenance | Typical | Easily Maintained |
| Time Duration | Long | Short |
| Re-usability | To some extent | Yes |
| Framework Type | Linear + Iterative | Linear |
| When Testing? | At the end of the engineering phase | After completion of development |
| Maintenance | Yes | Easily Maintainable |
| Detailed Documentation | Yes | Limited |
| Overlapping Phases | No | Yes |
More MCQs on Software Process Models
