What is rapid application development in software engineering?
RAD model in software engineering is the rapid application development model.
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a form of agile methodology that prioritizes the rapid prototype releases and iterations. RAD emphasizes the use of software and user feedback.
Instead of starting a development schedule from scratch each time, developers can make multiple iterations and updates to a software rapidly by following the RAD.
“rad model follows a component based approach”
Steps in Rapid Application Development
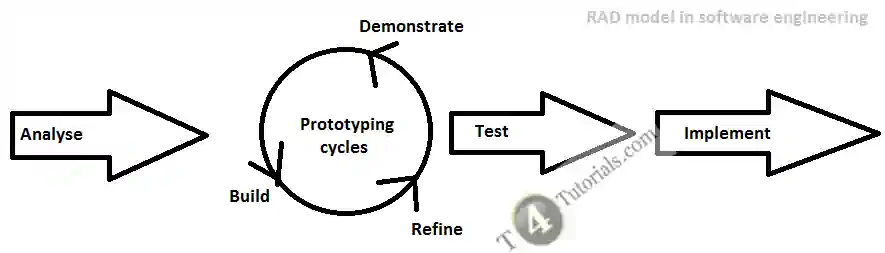
Four basic steps in RAD are mentioned below;
- Define the requirements
- Prototype
- Receive Feedback
- Finalize Software
1. Define the Requirements
RAD doesn’t require tthe requirement engineer to sit with end users and get a detailed list of software requirement specifications. RAD asks for a broad requirement.
2. Prototype
A
software prototype is a dummy software. When a customer gives us the requirement, we designed the
requirements fastly and make a prototype for software and show it to the customer to validate the requirements.
3. Receive Feedback
Software team receive the feedback from the customer and incorporate into the software.
4. Finalize Software
At last, functional and non-functional requirements validation is achieved with the help of customer.
Advantages of RAD
Encourages and priorities customer feedback.
Requirements can be changed at any time because in start there is no detailed and strong requirement management.
Reviews are quick in RAD to facilitate the customer.
Time between prototypes and iterations is short so team need to do it rapidly.
Development time is drastically reduced.
Integration isn’t a problem, since it integrates from project inception.
Rapidly and more production with fewer team members.
Disadvantages of RAD
RAD Needs highly skilled developers who can word rapidly.
RAD is more complex to manage as compared to other SDLC models.
RAD Needs user requirement throughout the life cycle of the product.
RAD Cannot work with large teams due to collaboration issues when team is large.
RAD is only helpful in the system where systems can be modularized.
RAD is only suitable for projects which small development time.
RAD Needs strong team collaboration to work rapidly.
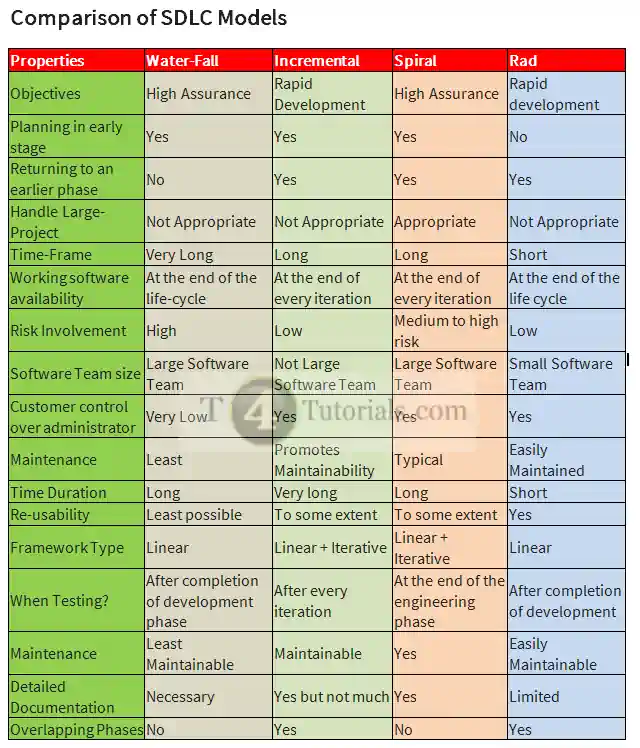
Comparison of RAD and waterfall model
| Properties |
Rad |
Water-Fall |
| Objectives |
Rapid development |
High Assurance |
| Planning in early stage |
No |
Yes |
| Returning to an earlier phase |
Yes |
No |
| Handle Large-Project |
Not Appropriate |
Not Appropriate |
| Time-Frame |
Short |
Very Long |
| Working software availability |
At the end of the life cycle |
At the end of the life-cycle |
| Risk Involvement |
Low |
High |
| Software Team size |
Small Software Team |
Large Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator |
Yes |
Very Low |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintained |
Least |
| Time Duration |
Short |
Long |
| Re-usability |
Yes |
Least possible |
| Framework Type |
Linear |
Linear |
| When Testing? |
After completion of development |
After completion of development phase |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintainable |
Least Maintainable |
| Detailed Documentation |
Limited |
Necessary |
| Overlapping Phases |
Yes |
No |
Comparison of RAD and incremental model
| Properties |
Rad |
Incremental |
| Objectives |
Rapid development |
Rapid Development |
| Planning in early stage |
No |
Yes |
| Returning to an earlier phase |
Yes |
Yes |
| Handle Large-Project |
Not Appropriate |
Not Appropriate |
| Time-Frame |
Short |
Long |
| Working software availability |
At the end of the life cycle |
At the end of every iteration |
| Risk Involvement |
Low |
Low |
| Software Team size |
Small Software Team |
Not Large Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator |
Yes |
Yes |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintained |
Promotes Maintainability |
| Time Duration |
Short |
Very long |
| Re-usability |
Yes |
To some extent |
| Framework Type |
Linear |
Linear + Iterative |
| When Testing? |
After completion of development |
After every iteration |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintainable |
Maintainable |
| Detailed Documentation |
Limited |
Yes but not much |
| Overlapping Phases |
Yes |
Yes |
Comparison of RAD and Spiral model
| Properties |
Rad |
Spiral |
| Objectives |
Rapid development |
High Assurance |
| Planning in early stage |
No |
Yes |
| Returning to an earlier phase |
Yes |
Yes |
| Handle Large-Project |
Not Appropriate |
Appropriate |
| Time-Frame |
Short |
Long |
| Working software availability |
At the end of the life cycle |
At the end of every iteration |
| Risk Involvement |
Low |
Medium to high risk |
| Software Team size |
Small Software Team |
Large Software Team |
| Customer control over administrator |
Yes |
Yes |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintained |
Typical |
| Time Duration |
Short |
Long |
| Re-usability |
Yes |
To some extent |
| Framework Type |
Linear |
Linear + Iterative |
| When Testing? |
After completion of development |
At the end of the engineering phase |
| Maintenance |
Easily Maintainable |
Yes |
| Detailed Documentation |
Limited |
Yes |
| Overlapping Phases |
Yes |
No |
a) Highly specialized & skilled team required due to increases re-usability of components
b) Increases re-usability of components
c) Encourages customer/client feedback
d) Highly specialized & skilled developers/designers are required
Answer - Click Here:
Answer: A
a) RAD Model
b) Prototyping Model
c)
Waterfall Model
d) None of above
Answer - Click Here:
Answer: A
More MCQs on Software Process Models
- Iterative Model MCQs
- Spiral Model MCQs
- incremental Model MCQs
- Software Process Models MCQs

 Four basic steps in RAD are mentioned below;
Four basic steps in RAD are mentioned below;

