Summary:
“Darkness” is a gothic and apocalyptic poem written by Lord Byron in 1816, a year famously known as the “Year Without a Summer” due to the eruption of Mount Tambora, which caused widespread climate abnormalities. The poem presents a grim and dystopian vision of the end of the world, where the sun ceases to shine, life deteriorates, and humanity descends into chaos. The poem describes a world consumed by darkness, where people burn cities for warmth, turn against each other for survival, and eventually perish, leaving Earth as a lifeless void. The themes of destruction, isolation, and existential despair dominate the poem, reflecting Byron’s deep pessimism about human nature. Written in blank verse (unrhymed iambic pentameter), the poem lacks a structured rhyme scheme, enhancing its chaotic and unsettling atmosphere. The tone is dark, hopeless, and apocalyptic, making it one of Byron’s most unique and haunting works.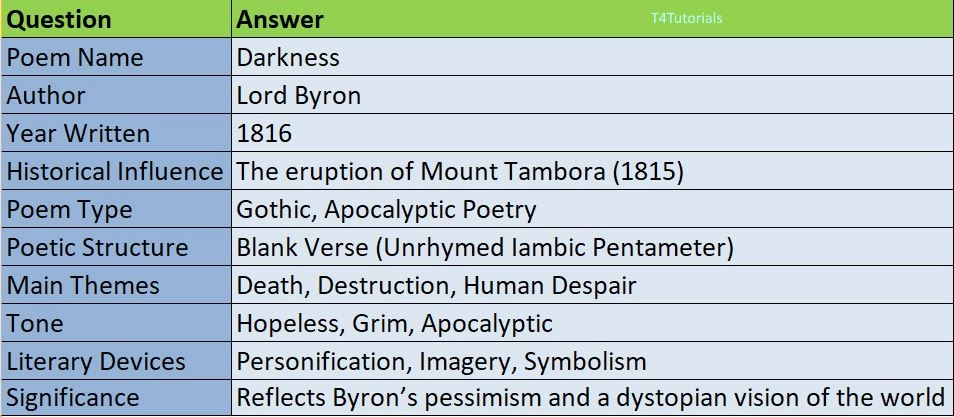
10
Score: 0
Attempted: 0/10
Subscribe
| Question | Answer |
| Poem Name | Darkness |
| Author | Lord Byron |
| Year Written | 1816 |
| Historical Influence | The eruption of Mount Tambora (1815) |
| Poem Type | Gothic, Apocalyptic Poetry |
| Poetic Structure | Blank Verse (Unrhymed Iambic Pentameter) |
| Main Themes | Death, Destruction, Human Despair |
| Tone | Hopeless, Grim, Apocalyptic |
| Literary Devices | Personification, Imagery, Symbolism |
| Significance | Reflects Byron’s pessimism and a dystopian vision of the world |