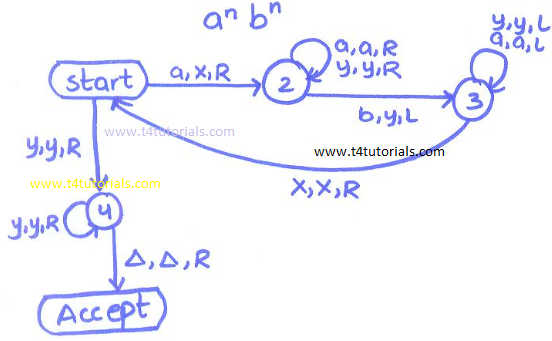
Turing Machine of equal a’s and b’s:
Suppose we want to design a Turing Machine for the language of anbn where a=b. Logic: If machine reads anyone a from the input tape, then machine write X and if machine reads any b then machine write y; a = X b = Y Purpose to make every a as X and to every b as Y is only to match one a with one b. This is the way to the bound equal number of a’s and b’s. Accepted strings: Such kind of strings should be accepted by Turing Machine. e.g, ab, aabb, aaabbb,…..etc. Rejected strings: Such kind of strings should be rejected by Turing Machine. e.g, abb, aab, aaabb,…..etc.
Read More Examples of Turing Machine
- Turing Machine to copy a string: with animations
- Turing Machine of numbers divisible by 3: with animations
- Turing machine for anbncn: with animations
-
Turing machine of two equal binary strings: with animations
-
Turing Machine to Accepts palindromes: with animations
-
Turing machine for a’s followed by b’s then c’s where the number of a’s multiplied by the number of b’s and equals to the number of c’s: with animations
-
Turing machine to Add two binary numbers: with animations
- Turing machine to Multiply two unary numbers: with animations
- Turing machine to Multiply two binary numbers: with animations
- Turing Machine for the complement of a string
- Turing Machine for the language of anbn where a=b.
- Turing Machine for a is less than b, ambn where a=b or m=n.
Turing machine for the language of all those string in which a is less than b