Summary:
“The Giaour” is a narrative poem by Lord Byron, first published in 1813 as part of his Oriental Tales series. The title, Giaour, is a derogatory Turkish term for a non-Muslim or infidel. The poem is set in the Ottoman Empire and follows a fragmented, nonlinear storytelling structure.
The story revolves around Leila, a woman from the Ottoman ruler Hassan’s harem, who is executed for being unfaithful. Her lover, a Venetian Christian warrior known as the Giaour, avenges her death by killing Hassan. However, this act of revenge does not bring him peace, and he later retreats to a monastery, haunted by guilt and remorse. The poem explores themes of revenge, love, faith, fate, and existential despair.
Byron’s The Giaour introduced a new type of literary figure: the Byronic Hero, a brooding, passionate, rebellious, and often tormented character. The poem is written in heroic couplets, blank verse, and varied meters, giving it a dramatic and lyrical style.
Score: 0
Attempted: 0/10
Subscribe
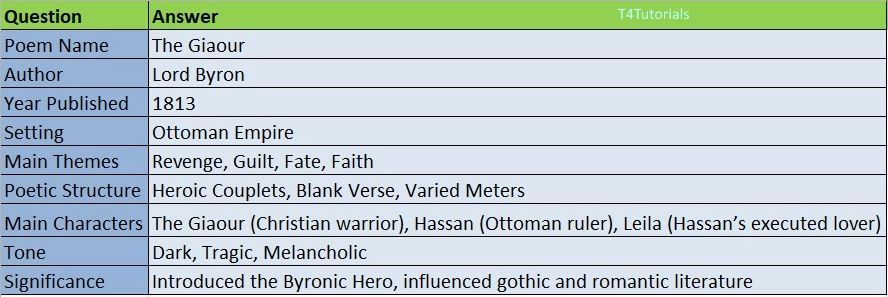
| Question | Answer |
| Poem Name | The Giaour |
| Author | Lord Byron |
| Year Published | 1813 |
| Setting | Ottoman Empire |
| Main Themes | Revenge, Guilt, Fate, Faith |
| Poetic Structure | Heroic Couplets, Blank Verse, Varied Meters |
| Main Characters | The Giaour (Christian warrior), Hassan (Ottoman ruler), Leila (Hassan’s executed lover) |
| Tone | Dark, Tragic, Melancholic |
| Significance | Introduced the Byronic Hero, influenced gothic and romantic literature |