What is an Attribute?
The attribute can be defined as a field for storing the data that represents the characteristics of a data object. The attribute is the property of the object. The attribute represents different features of the object.
For example, hair color is the attribute of a lady. Similarly, rollno, and marks are attributes of a student. An attribute vector is commonly known as a set of attributes that are used to describe a given object.
Example of attribute
In this example, RollNo, Name, and Result are attributes of the object named as a student.
| Rollo | Name | Result |
| 1 | Ali | Pass |
| 2 | Akram | Fail |
Type of attributes
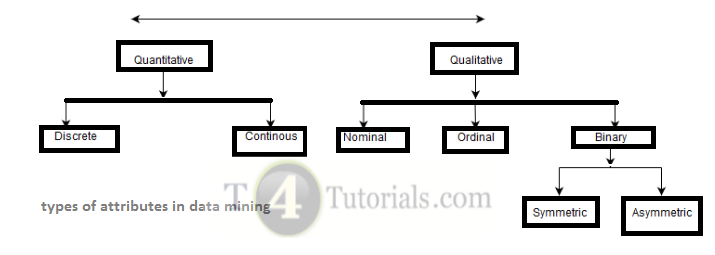
We need to differentiate between different types of attributes during Data-preprocessing. So firstly, we need to differentiate between qualitative and quantitative attributes.
1. Qualitative Attributes such as Nominal, Ordinal, and Binary Attributes.
2. Quantitative Attributes such as Discrete and Continuous Attributes. There are different types of attributes. some of these attributes are mentioned below;
- Binary
- Nominal
- Ordinal Attributes
- Numeric
- Interval-scaled
- Ratio-scaled
Nominal Attributes
Nominal data is in alphabetical form and not in an integer. Nominal Attributes are Qualitative Attributes.
Examples of Nominal attributes
| Attribute | Value |
| Categorical data | Lecturer, Assistant Professor, Professor |
| States | New, Pending, Working, Complete, Finish |
| Colors | Black, Brown, White, Red |
Binary Attributes
Binary data have only two values/states. For example, here HIV detected can be only Yes or No. Binary Attributes are Qualitative Attributes.
Examples of Binary Attributes
| Attribute | Value |
| HIV detected | Yes, No |
| Result | Pass, Fail |
The binary attribute is of two types;
Examples of Binary Attributes
| Attribute | Value |
| HIV detected | Yes, No |
| Result | Pass, Fail |
Examples of Asymmetric data
Both values are not equally important. For example, HIV detected is more important than HIV not detected. If a patient is with HIV and we ignore him, then it can lead to death but if a person is not HIV detected and we ignore it, then there is no special issue or risk.
Example
| Attribute | Value |
| HIV detected | Yes, No |
| Result | Pass, Fail |
Ordinal Attributes
All Values have a meaningful order.
Examples of Ordinal Attributes
For example, Grade-A means highest marks, B means marks are less than A, C means marks are less than grades A and B, and so on. Ordinal Attributes are Quantitative Attributes.