Optimal Page replacement Memory Management Operating Systems OS
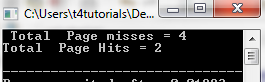
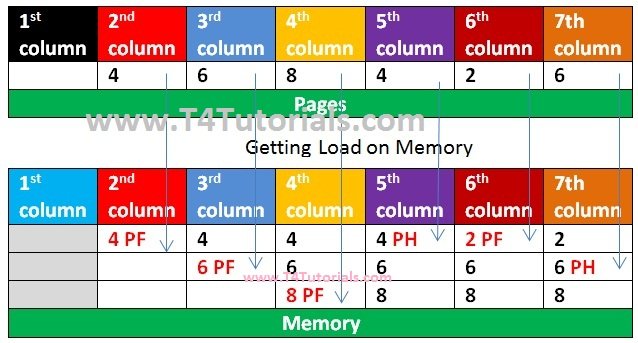
According to Optimal Page replacement OS replaces the page from the memory that is not used for a long period of time.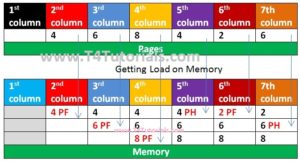
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 |
// CPP program for optimal <a href="https://t4tutorials.com/page-fault-page-replacement-operating-systems-os/">page page replacement algorithm in operating systems</a> #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Page exists in memory or not? bool PageSearch(int number, vector<int>& Frames) { for (int loop = 0; loop < Frames.size();loop ++) if (Frames[loop] == number) return true; return false; } // Fins unused Frames int predict(int page[], vector<int>& Frames, int pn, int index) { int res = -1, farthest = index; for (int loop = 0; loop < Frames.size();loop ++) { int loop2; for (loop2 = index; loop2 < pn; loop2++) { if (Frames[loop] == page[loop2]) { if (loop2 > farthest) { farthest = loop2; res = loop; } break; } } // Suppose the page is never referenced in future, if (loop2 == pn) return loop; } // If all of the Frames were not in future, // return any of them, we return 0. Otherwise // we return res. return (res == -1) ? 0 : res; } void optimalAlgorithm(int page[], int pn, int TotalFrames) { vector<int> Frames; // Traverse array with page reference array to check for the PageHit and miss. int PageHit = 0; for (int loop = 0; loop < pn; loop++) { // Page detected in memory if (PageSearch(page[loop], Frames)) { PageHit++; continue; } // Page not detected in memory if (Frames.size() < TotalFrames) Frames.push_back(page[loop]); // Find the page to be replaced. else { int loop2 = predict(page, Frames, pn, loop + 1); Frames[loop2] = page[loop]; } } cout << " Total Page misses = " << pn - PageHit << endl; cout << "Total Page Hits = " << PageHit << endl; } int main() { int page[] = { 4, 6, 8, 4, 2, 6 }; int pn = sizeof(page) / sizeof(page[0]); int TotalFrames = 3; optimalAlgorithm(page, pn, TotalFrames); return 0; } |