Shortest Job First Scheduling SJF Process Scheduling in operating systems.
The process with less burst time will always execute first.
Shortest job first scheduling is a non-preemptive scheduling algorithm so processes priority does not matter.
Preferred to minimize waiting time.
Better than First come first served scheduling.
Works only when the processor knows in advance that how much time every process will take to execute on CPU.
Not preferred for interactive systems because required CPU time is not already in knowledge.
Easy to implement in Batch systems because in batch systems CPU time is already known.
| Process | Burst Time | Arrival |
| P1 | 4 | 2nd |
| P2 | 2 | 3rd |
| P3 | 8 | 1st |
| P4 | 3 | 4th |
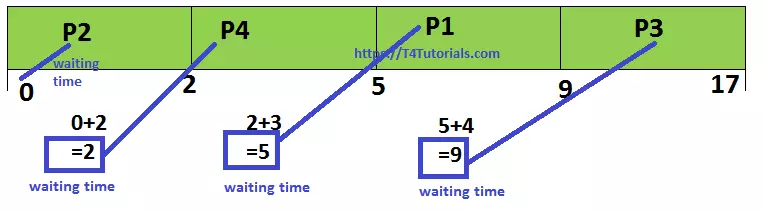
Gantt Chart Diagram of Short Job First Scheduling (SJF)
Let us see the Gantt Chart Diagram of Short Job First Scheduling (SJF).
| Process | Waiting Time |
| P1 | 5 |
| P2 | 0 |
| P3 | 9 |
| P4 | 2 |
Average Wait Time: (0+2+5+9) / 4 = 4
How to calculate turn around time?
TurnAroundTime = BurstTime + WaitingTime.
Advantages and disadvantages of shortest job first scheduling algorithm
Advantages of Shortest job first scheduling
Here are the benefits/pros of using Shortest job first process scheduling technique:
- Shortest job first process scheduling reduces the average waiting time over First in First Out algorithm.
- Probably optimal with regard to average turnaround time.
- Shortest job first process scheduling technique gives the lowest average waiting time for a specific set of processes.
- Shortest job first process scheduling is appropriate for the jobs running in batch, where run times are known in advance.
- For the batch system of long-term process scheduling, a burst time estimate can be obtained from the job description.
- Shortest job first process scheduling is frequently used for long term process scheduling.
- For Short-Term Process scheduling, we need to predict the value of the next burst time.
Disadvantages/Cons Shortest job first scheduling
Here are some drawbacks/cons of Shortest job first process scheduling algorithm:
- Shortest job first process scheduling algorithm may cause very long turnaround times or in other words we can say that it leads to the problem of starvation(aging is the solution to starvation).
- In Shortest job first process scheduling, elapsed time should be recorded, that results in more overhead on the processor.
- Operating system must know the Job completion time earlier, but it is easy to say but its hard to predict earlier.
- Shortest job first process scheduling is often used in a batch system for long term process scheduling.
- Shortest job first process scheduling requires knowledge of how long a process or job will run.
- It is hard to know the length of the upcoming CPU request in shortest job first process scheduling.
- We can’t implement the Shortest job first process scheduling for CPU process scheduling for the short term. It is because there is no specific technique to predict the length of the upcoming CPU burst.
- Shortest job first process scheduling leads to the starvation that does not reduce average turnaround time.
Non-Preemptive SJF
In non-preemptive process scheduling, once the CPU cycle is allocated to shortest process, then this process holds the resources until it reaches a waiting state or terminated by the operating system.
Preemptive SJF
In Preemptive SJF Scheduling, when a process comes then operating system put it into the ready queue. A process with shortest burst time starts it execution. Now, If some new process with shortest than shortest time arrives, in this case the current process is removed from execution, and the shorter than shortest process will win the CPU cycle.
Program of Shortest Job First Scheduling (SJF) in C Language
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int BurstTime[20];
int p[20];
int WaitingTime[20];
int TurnAroundTime[20];
int TotalProcesses, i, j;
int total=0;
int pos,temp;
float avg_WaitingTime,avg_TurnAroundTime;
printf("Enter total number of process:");
scanf("%d",& TotalProcesses);
printf("\nEnter Burst Time for each process:\n");
for(i=0;i<TotalProcesses;i++)
{
printf("p%d:",i+1);
scanf("%d",&BurstTime[i]);
p[i]=i+1;
//code for process number
}
//sorting burst time in ascending order by sorting with selection sort
for(i=0;i<TotalProcesses;i++)
{
pos=i;
for(j=i+1;j<TotalProcesses;j++)
{
if(BurstTime[j]<BurstTime[pos])
pos=j;
}
temp=BurstTime[i];
BurstTime[i]=BurstTime[pos];
BurstTime[pos]=temp;
temp=p[i];
p[i]=p[pos];
p[pos]=temp;
}
WaitingTime[0]=0;
//waiting time for first process will be zero
//calculate waiting time
for(i=1;i<TotalProcesses;i++)
{
WaitingTime[i]=0;
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
WaitingTime[i]+=BurstTime[j];
total+=WaitingTime[i];
}
avg_WaitingTime=(float)total/TotalProcesses;
//average waiting time
total=0;
printf("\nProcess\t Burst Time \tWaiting Time\tTurnaround Time");
for(i=0;i<TotalProcesses;i++)
{
TurnAroundTime[i]=BurstTime[i]+WaitingTime[i];
//calculate turnaround time
total+=TurnAroundTime[i];
printf("\np%d\t\t %d\t\t %d\t\t\t%d",p[i],BurstTime[i],WaitingTime[i],TurnAroundTime[i]);
}
avg_TurnAroundTime=(float)total/TotalProcesses;
//average turnaround time
printf("\n\nAverage Waiting Time=%f",avg_WaitingTime);
printf("\nAverage Turnaround Time=%f\n",avg_TurnAroundTime);
}
Code of SJFS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int bt[20],p[20],wt[20],tat[20],i,j,n,total=0,pos,temp;
float avg_wt,avg_tat;
printf("Enter number of process:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\nEnter Burst Time:\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("p%d:",i+1);
scanf("%d",&bt[i]);
p[i]=i+1; //contains process number
}
//sorting burst time in ascending order using selection sort
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
pos=i;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(bt[j]<bt[pos])
pos=j;
}
temp=bt[i];
bt[i]=bt[pos];
bt[pos]=temp;
temp=p[i];
p[i]=p[pos];
p[pos]=temp;
}
wt[0]=0; //waiting time for first process will be zero
//calculate waiting time
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
wt[i]=0;
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
wt[i]+=bt[j];
total+=wt[i];
}
avg_wt=(float)total/n; //average waiting time
total=0;
printf("\nProcess\t Burst Time \tWaiting Time\tTurnaround Time");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
tat[i]=bt[i]+wt[i]; //calculate turnaround time
total+=tat[i];
printf("\np%d\t\t %d\t\t %d\t\t\t%d",p[i],bt[i],wt[i],tat[i]);
}
avg_tat=(float)total/n; //average turnaround time
printf("\n\nAverage Waiting Time=%f",avg_wt);
printf("\nAverage Turnaround Time=%f\n",avg_tat);
return 0;
}
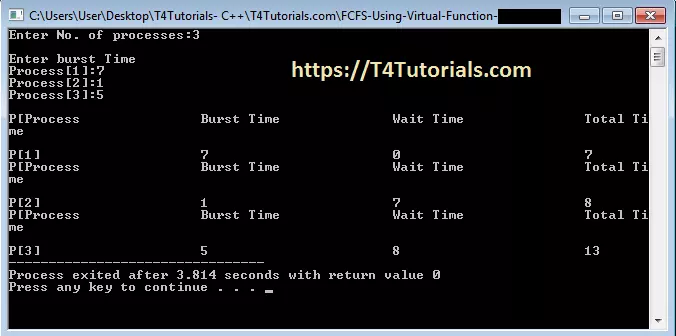
Output
SJF implementation in Java
Let us see the SJF implementation in Java.
import java.util.*;
public class SJF {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println ("enter no of process:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
int process_id[] = new int[n];
int complete_time[] = new int[n];
int arrival_time[] = new int[n];
int burst_time[] = new int[n];
int turn_around_time[] = new int[n];
int waiting_time[] = new int[n]; //wt means waiting time
int f[] = new int[n]; // f means it is flag it checks process is completed or not
int st=0, total_processes=0;
float avgwt=0, avgta=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.println ("enter process " + (i+1) + " arrival time:");
arrival_time[i] = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println ("enter process " + (i+1) + " brust time:");
burst_time[i] = sc.nextInt();
process_id[i] = i+1;
f[i] = 0;
}
boolean a = true;
while(true)
{
int c=n, min=999;
if (total_processes == n)
break;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
/*
* If i'th process arrival time is less than or equal to system time and its flag=0 and burst<min
* this process will be first
*/
if ((arrival_time[i] <= st) && (f[i] == 0) && (burst_time[i]<min))
{
min=burst_time[i];
c=i;
}
}
/* If c==n means c value can not updated because no process arrival time< system time so we increase the system time */
if (c==n)
st++;
else
{
complete_time[c]=st+burst_time[c];
st+=burst_time[c];
turn_around_time[c]=complete_time[c]-arrival_time[c];
waiting_time[c]=turn_around_time[c]-burst_time[c];
f[c]=1;
total_processes++;
}
}
System.out.println("\npid arrival brust complete turn waiting");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
avgwt+= waiting_time[i];
avgta+= turn_around_time[i];
System.out.println(process_id[i]+"\t"+arrival_time[i]+"\t"+burst_time[i]+"\t"+complete_time[i]+"\t"+turn_around_time[i]+"\t"+waiting_time[i]);
}
System.out.println ("\naverage tat is "+ (float)(avgta/n));
System.out.println ("average wt is "+ (float)(avgwt/n));
sc.close();
}
}
Video Lecture
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the average turnaround time for these processes with the SJF scheduling algorithm?
Gantt Chart for SJF
Process: 1 3 2
|—————|–|——–|
Time : 0 8 9 13
Average Turnaround Time: ( (8-0)+(13-0.4)+(9-1.0) ) / 3 = 9.53
The preemptive version of shortest-job-first-scheduling is called shortest-remaining time first.
The kernel is preemptive?
T/F
[su_spoiler title=”Answer – Click Here:” class=”padding: -10px;”]Answer: False, the kernel is nonpremptive[/su_spoiler]
Another word for nonpreemptive is ___?
[su_spoiler title=”Answer – Click Here:” class=”padding: -10px;”]Answer:cooperative[/su_spoiler]
Preemptive scheduling needs ____ such as a timer.
[su_spoiler title=”Answer – Click Here:” class=”padding: -10px;”]Answer:hardware support[/su_spoiler]
SJF Scheduling is preemptive or non preemptive?
[su_spoiler title=”Answer – Click Here:” class=”padding: -10px;”]Answer:SJF can be preemptive or nonpreemptive.[/su_spoiler]