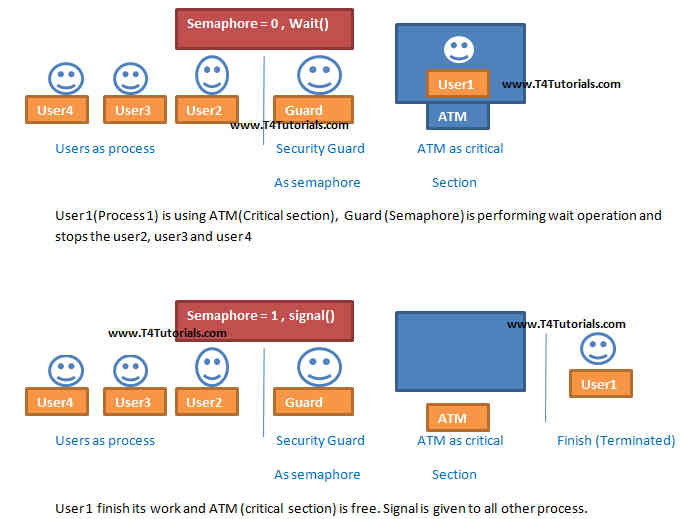
What are semaphores?
Semaphores are the variables. Semaphores are used for signaling among processes. Three kinds of operations are performed on semaphores;- To initialize the semaphore
- To increment the semaphore value
- To decrement the semaphore value
What are binary semaphores?
Binary semaphores take only the values between 0 to 1.What are counting semaphores?
Counting semaphores have the non-negative integer value.How can processes get the critical section?
- A critical section is controlled by semaphores by following operations;
- Wait:
- Any process can’t enter into the critical section.
- The semaphore value is decremented.
- Signal:
- The process can enter into the critical section.
- The semaphore value is incremented.
- Wait:

Wait and Signal Operations in Semaphores
We can implement Wait and Signal Operations in process synchronization. The actual purpose of Wait and Signal operation is to get mutual exclusion.The Wait Operation in Semaphores
The wait operation decrements the value of Semaphore if it is positive. If Semaphore is negative or zero, then no operation is performed.wait(Semaphore) { while (Semaphore<=0); Semaphore–; }
Signal Operation in Semaphores
The signal operation increments the value of Semaphore.signal(Semaphore) { Semaphore++; }
Semaphores implementation in C++
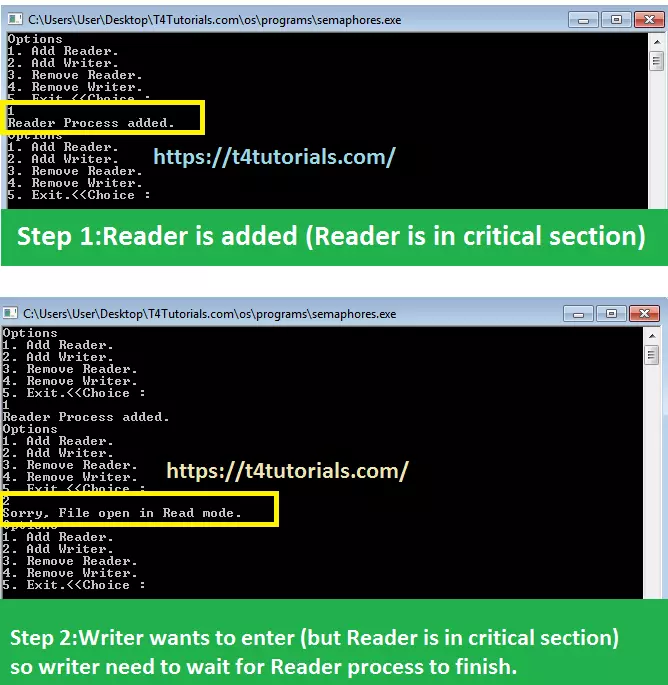
Now, let’s see theC++ Program for Semaphores.|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 |
#include<iostream> #include<mutex> using namespace std; struct semaphore { int mutex; int rcount; int rwait; bool wrt; }; void addReader(struct semaphore *s) { if(s->mutex == 0 && s->rcount == 0) { cout<<"Sorry, File isopen in Write mode.\nNew Reader added to queue."<<endl; s->rwait++; } else { cout<<"Reader Process added."<<endl; s->rcount++; s->mutex--; } return ; } void addWriter(struct semaphore *s) { if(s->mutex==1) { s->mutex--; s->wrt=1; cout<<"\nWriter Process added."<<endl; } else if(s->wrt) cout<<"Sorry, Writer already operational."<<endl; else cout<<"Sorry, File open in Read mode."<<endl; return ; } void removeReader(struct semaphore *s) { if(s->rcount == 0) cout<<"No readers to remove."<<endl; else { cout<<"Reader Removed."<<endl; s->rcount--; s->mutex++; } return ; } void removeWriter(struct semaphore *s) { if(s->wrt==0) cout<<"No Writer to Remove"<<endl; else { cout<<"Writer Removed"<<endl; s->mutex++; s->wrt=0; if(s->rwait!=0) { s->mutex-=s->rwait; s->rcount=s->rwait; s->rwait=0; cout<<"waiting Readers Added:"<<s->rcount<<endl; } } } int main() { struct semaphore S1={1,0,0}; while(1) { cout<<"Options"<<endl<<"1. Add Reader."<<endl<<"2. Add Writer."<<endl<<"3. Remove Reader."<<endl<<"4. Remove Writer."<<endl<<"5. Exit.<<Choice : "<<endl; int choice; cin>>choice; switch(choice) { case 1: addReader(&S1); break; case 2: addWriter(&S1); break; case 3: removeReader(&S1); break; case 4: removeWriter(&S1); break; case 5: cout<<"\n\tGoodBye!";break; default: cout<<"\nInvalid Entry!"; } } return 0; } |
Difference between Binary Semaphore VS Counting Semaphore
Let’s see some common difference between binary and counting semaphore:| Binary Semaphore | Counting Semaphore |
| Mutual exclusion | No mutual exclusion |
| Semaphore Value is only 0 and 1 | Semaphore Value is any integer value |
| The only process at the same time. | Can provide a set of Processes |
| Only one slot | More than one slot |
Advantages of Semaphores
Some of the advantages of semaphores are mentioned below:- Semaphores strictly follow the principle of mutual exclusion and allow only one process into the critical section at the same time.
- Semaphores are machine-independent, so Semaphores are implemented in the machine-independent code of the microkernel.
- Semaphores allow flexible management of resources.
- Semaphores can be considered as more efficient than other methods of synchronization.
Disadvantages of Semaphores
Some of the disadvantages of semaphores are mentioned below;- Semaphores are very complex to implement, so the wait and signal operations must be implemented in the correct order. If the wait and signal operations are not implemented in the correct order, then it can be a cause of a deadlock.
- Semaphores can be lead to priority inversion. In priority inversion, low priority processes may win the critical section and access first, and high priority processes get the critical section after the low priority process.
- The operating system needs to do some extra work and maintains track of all calls to wait and signal operations in semaphore.