Simplex, Half duplex, Full-duplex Data Transmission Modes
Transmission Mode
The transmission mode is the way of transferring data between two devices. It is also known as communication mode. Buses and networks are formed in such a way to allow communication to occur between individual devices that are interconnected. There are three types of transmission mode:-
Types of Transmission Mode
There are three types of transmission modes in computer networks
- Simplex mode
- Half-duplex mode
- Full-duplex mode
Simplex Mode
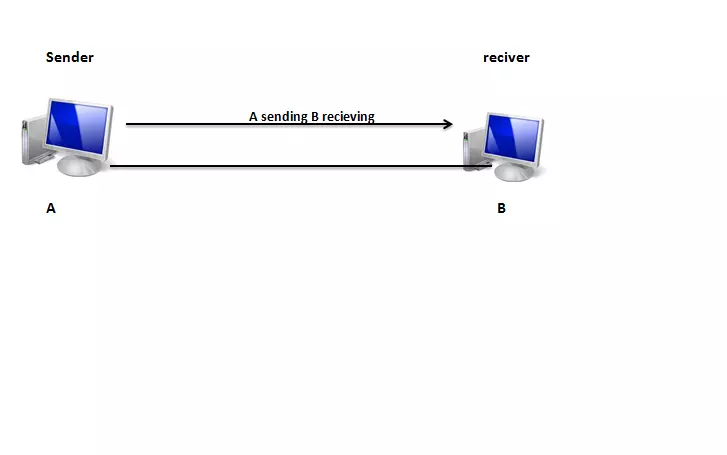
In simplex mode data transmitted on only one side.it means only one device can send a signal. In a
simplex mode of transmission, the communication is unidirectional
In a
simplex transmission mode, the communication between the sender and receiver performed only in one direction. That means only the sender device can send the data, and a receiver device can only receive the data. The receiver is not able to resend or communicate in reverse to the sender.
Example of Simplex Mode
One way traffic road id an example of Simplex mode.in the way the traffic travels in only one way.No vehicle can enter from the opposite side of the road.the all capacity is used by the sender.
Another example we can put about the simplex mode is Keyboard or Mouse.
The keyboard only able to send input to monitor, and the monitor is only receiving input from the keyboard, and display on the screen. The monitor is not able to send again data to keyboard.
Advantage of Simplex mode
- The full capacity of the transmission medium is used by the sender.
- It is a very simple way of transmission.
- It has no traffic issues.
Disadvantages of Simplex Mode
- There is only one way of transmission
- There is ni bidirectional communication is possible.
- Two devices cannot communicate in simplex mode.
Half-Duplex Mode
In a half-duplex mode, data can be transmitted in both ways. Both devices can send or receive data in both directions but not at the same time. When one device can send signals, the other only receive. The half Duplex mode used in situations where there is no need for transmission on both sides at the same time. The whole capacity of a network can be used in one direction at a time. In half-duplex mode transmission can be done both ways which means if two systems are connected with the half-duplex mode of transmission, they both can send and receive data but not the same simultaneously. If one device is sending data then another device cannot send data until it receives the data which is already in transmission. You can say that communication is not simultaneous.

Example of Half-duplex Mode
Walkie-Talkie is big example of half Duplex mode.in which message is send in both direction but not in the same time .when one person send a text other can only receive it, and one person when finishing his message than other one is able to send message
Another example of half-duplex mode is radio communication devices.
In the battlefield soldiers used this device for communication,
In this away when one man sending its message, a man on another hand only received it, When first-person say over than another person will be able to send a message, same as a mobile phone.
Advantages of Half-Duplex Mode
- Speed is a big advantage of a full-duplex.
- The device can receive and send data, but not at the same time.
- Troubleshooting is very easy
- Data is transmitted in both sides
- It provides bidirectional communication.
Disadvantages of Half Duplex mode
- In a half Duplex, moe data cannot be transmitted in both side in the same time
- When one device sending data, the device on the other hand only receive data.
- It is slow in data transmission.
- Delay in data transmission.
Full-Duplex Mode
In full-duplex mode, data is transmitted in both directions at the same time. Sender and receiver can send data at the same time. The entire capacity of the channel is shared between both devices. The capacity can be shared between both sides in two ways.
- You physically share the link between the sender and receiver.
- In a
 second way, you can share capacity through signals .signal can travel from one side to the opposite side.
second way, you can share capacity through signals .signal can travel from one side to the opposite side.
Example of Full-Duplex Mode
The big example of full-duplex mode is a telephone, In telephone conversion, both people are able to speak and listen
Another example of full-duplex mode is two-way traffic in which vehicles can enter from opposite sides
Advantages of Full-duplex Mode
- performance of full-duplex mode is much batter than half and simplex mode.
- The speed of full-duplex mode is high than simplex and half-duplex mode.
- Data can be sent and receive on both sides, which increases the performance of the network.
- No delay in communication, because both devices send and receive data at the same time.
Disadvantages of Full-duplex Mode
- No proper bandwidth utilization as the same line is used for sending and receiving data at the same time.
- It is more complex than a simplex and half-duplex mode
Main Differences between the Three Transmission Modes
- In simplex mode, the data or signal is sent in one direction. In half-duplex mode, the signal can be transmitted in both directions, but one at a time. While In full-duplex mode, the signal is sent in both directions at the same time.
- In simplex mode, only one device can send the signal. In half-duplex mode, both devices able to transmit the signal, but not at the same time. In full-duplex mode, both devices can transmit the signal at the same time.
- Full-duplex performance is much better than half-duplex and half-duplex.
- Simplex: The example of simplex mode is the keyboard sends the data to the monitor. The monitor cannot reply to the keyboard.
- Half-duplex: The walkie-talkie is the big example of half-duplex mode, both speakers can communicate, but they have to take turns.
- Full duplex: Using a telephone, both speakers can communicate at the same time.
Compression Table of Simplex Mode, Half-Duplex Mode, and Full-Duplex Mode
| Basis Of Compression |
Simplex |
Half Duplex |
Full Duplex |
| Direction of Communication |
Data transmitted only in one direction at a time |
Signals can be transmitted on both side, but not at the same time |
Signals can be transmitted on both sides at the same time. |
| Send / Receive |
The sender only send data |
The sender can be sent and receive but not at the same time |
The sender can send and receive data at the same time |
| Performance |
Worst performance |
Batter performance |
Best performance |
| Example |
Keyboard |
Walkie-talkie |
Telephone |
 There are three types of transmission modes in computer networks
There are three types of transmission modes in computer networks


 second way, you can share capacity through signals .signal can travel from one side to the opposite side.
second way, you can share capacity through signals .signal can travel from one side to the opposite side.