What is DOM(Document object model)?
The HTML page is a collection of object called “Elements” and these elements are called “DOM Elements. Document Object Model Is basically a map or model of a web page. Its job is to describe the structure of an HTML document and the relationship between different elements like tags, attributes, and texts on a page. If we doing addition, deletion or modification in existing element on our website, so basically we are developing the structure of DOM. As a W3C specification, one important objective for the Document Object Model is to provide a standard programming interface that can be used in a wide variety of environments and applications. The Document Object Model can be used with any programming language. Every DOM obj. is different and It has its own “properties, events and functionality”. And every DOM obj. has its own Documentation, according to “DOM standard”. There are additional documented functions that can be used to manage an element. These are called the DOM API. There are three types of API’s which are specified by DOM Standard:- Properties
- Events
- Methods
-
Example 1 of DOM:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
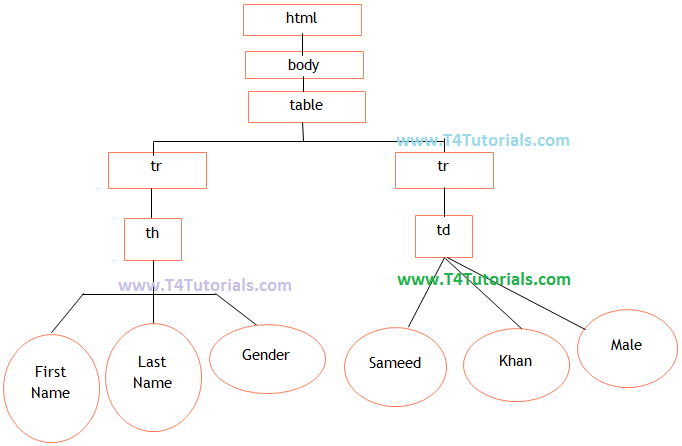
<span style="font-size: 14pt;"><html> <body> <Table> <tr> <th>Firstname</th> <th>Lastname</th> <th>Gender</th> </tr> <tr> <td>Sameed</td> <td>Khan</td> <td>Male</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html></span> |
- Now you can see the DOM representation of this code

Figure: DOM Tree
Example 2 of DOM:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
<span style="font-size: 14pt;"><html> <head> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1></h1> </body></html></span> |

-
Why is DOM used for?
- Add DOM elements to a tree
- Remove DOM elements
- Add, Remove or Modify attributes.
-
DOM History
- There are two model of DOM
- Model 1 concentrates on HTML and XML DOM. Model 1 contains the functionality for having document navigation and management. level 1 became a 1st recommendation of W3C in October 1998.
- Model 2 became a recommendation of W3C on 13 November 2000. In this, we can add the style object to the DOM to manage the style information in the document. Level 2 also defines an event model and provide the support for XML namespaces.
-
Advantages of DOM
- XML DOM provides us platform and independence in languages.
- XML DOM is traversable.
- XML DOM is editable and dynamic. It allows developers to do addition, updating, deletion or move nodes on the tree.
- Robust API for the DOM tree.
- Relatively simple to modify the data structure and extract data.
-
Disadvantages of DOM
- It consumes more memory when the XML structure becomes large.
- Its operational speed is slower due to the larger usage of memory.
- Stores the entire document in memory.
- As DOM was written for any language, method naming conventions don’t follow standard Java programming conventions.
-
When to use DOM?