Guess Paper 1 : Advanced Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Advanced Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Fall – 2020 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q1. (a) Explain Class A, B, & C amplifiers in detail. (b) Explain Common-Collector amplifier. Q2. (a) Derive a relation for total gain of 3-stage cascaded amplifier. (b) Explain different coupling methods in amplifiers. Q3. Explain switched capacitor DAC with the help of circuit diagram. Q4. Briefly explain RC &LC filters with circuit diagrams used in amplifier circuits. Q5. (a) Write a detail notes on Series and Shunt regulators. (b) What is the difference between voltage regulators and voltage multipliers? Q6. With the help of diagram, explain Flash A/D convertor in detail. Q7. (a) Explain Push-Pull Amplifier in detail. (b) Define Harmonic distortion and Feedback in amplifiers. Q8. Write short note on any two of the following- ADC performance and Specification.
- R-2R Ladder DAC.
- Voltage variable capacitor.
Guess Paper 2 : Advanced Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Advanced Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Spring – 2020 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q.1. Define the following terms properly. (14)- Passive filters
- Uni-junction Transistor (UJT)
- Small signal and Large signal analysis (Amplifier)
- Step-up and step-down transformers
- Positive and Negative Feedbacks
- Integrated circuits (ICs)
- Cross-over distortion
- B) Differentiate between series and shunt regulators. Explain your answer with the help of circuits if needed.
- B) Class-C amplifier is the most efficient than class A, class-B or class-AB amplifiers.
- Discuss class C power dissipation
- Calculate maximum efficiency
- Calculate maximum power output
- Methods of coupling
- Optoelectronic devices (Photodiode and phototransistor)
- Darlington pair
- Voltage multipliers (Doubler and Tripler)
Guess Paper 3 : Basic Electronics
University Name – Confidential
- b) Discuss the internal circuit of DC voltmeter
- b) Draw the logic diagram for a general ADC.
- b) A 20V dc voltage is measured by analog and digital multi-meters. The analog instrument is on its 25 V range, and its specified accuracy is 2% the digital meter has a 3.5 digital display and an accuracy of(0.6+1). Determine the measurement accuracy in each case.
- b) When the given circuit is in resonance. E=100 mV, R = 5 Ohms and XL= Xc= 100 Ohms. Calculate the Q factor.
- Thermocouple instruments
- Unregulated DC power supply
- Low frequency signal generator
Guess Paper 4: Digital Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Digital Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Spring – 2020 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q-1. Differentiate among the following terms. (14)- Analog and Digital quantities
- OR & AND logic operations
- Multiplexer and Demultiplexer
- RAM and ROM types of memories
- Encoding and Decoding
- SOP (min-terms) and POS (max-terms)
- Combinational and sequential logic
- (B52.F16)16 = (_________________)2
- (10010101)2 = (_________________)10
- (786.75)10 = (___________________)2
- Convert the binary number (1100011)2 to Gray Code
- 2’s complement of (100101)2?
- Parallel Binary Adders
- Counter designing
- Programmable Logic Arrays
Guess Paper 5: Digital Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Digital Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Fall – 2020 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q.1. Answer the following short questions: (14)- Differentiate between analog and digital quantities.
- Convert (5C.8)16 into binary number i.e. (——————————)
- Find the 2’s compliment of the given binary number i.e.
- The given ASCII character 00110111 is received by an odd parity system. Is it correct?
- Draw pulse/timing diagram for the number
- Add the given BCD numbers properly. 10000110+00010011.
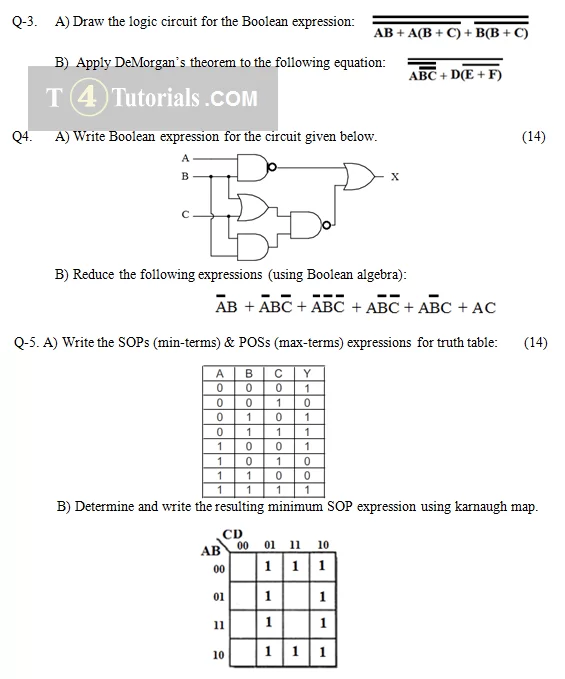
- Draw logic diagram for the Boolean expression:
- B) Minimize the under given SOP expression using the Karnaugh map:
- B) Describe the operation, logic diagram and truth table for JK flip-flop. Also describe that how JK flip-flop is different than SR.
- B) Convert the following Gray codes to Binary using logic gates.
- 1100011 ii. 1001101
- B) Differentiate between Multiplexer & Demultiplexer. Design 1-to-8-lines DEMUX.
- What is the universal property of NAND or NOR gate? Explain.
- Describe a 3-Bit ripple/asynchronous binary counter.
- Differentiate among the TTL, ECL and CMOS integrated circuits.
- Analyze the internal logic of a magnitude comparator that has both equality and in-equality outputs.
Guess Paper 6: Basic Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Basic Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Fall – 2018 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q.1 Fill in the blanks [14 Marks]- The Naturally Pure Semiconductor is called …………Semiconductor.
- The Majority carriers in N-Type semiconductor is …………………………………
- The Device/Element have the ability of rectification is known as ______________.
- The _______ is current controlled and Uni-Polar device .
- BJT stand for_______.
- IGFET stand for………
- The SCR stand for…………………………………………………
Guess Paper 7: Basic Electronics
University Name – Confidential
NOTE: Q.1 is compulsory, attempt any four questions from the remaining. All questions carry equal marks. Phones and other Electronic Gadgets are not allowed. Paper : Basic Electronics Time Allowed: 3 hours Examination: Final, Fall – 2017 Total Marks: 70, Passing Marks (35) Q.1 Fill in the blanks [14 Marks]- The Naturally Pure Semiconductor is called …………Semiconductor.
- The Majority carriers in P-Type semiconductor is …………………………………
- The Device/Element have the ability of amplification is known as ______.
- The Diode having the ability of Voltage regulation is known as _______.
- MOSFET stand for_______.
- SCR stand for………
- The Diode Limiter is also called?