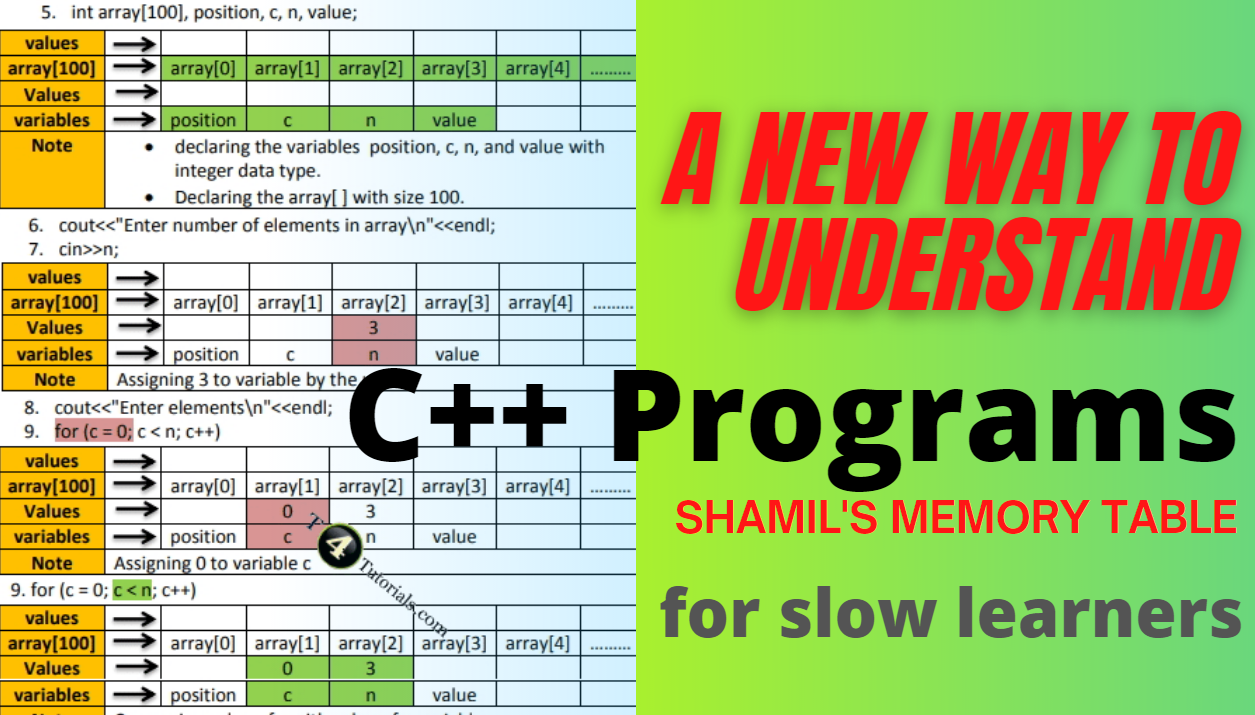
SFT is the artificial representation of the program flow and in this representation, we represent the flow of the program by keeping in view the line number of the written program.Special precautions you need some special precautions while writing the SFT. For example, if you add some new line of code in your program, then you must change SFT accordingly. Components of SFT The scenario of program Pre-line and post-line are the two major components of the SFT. Let’s see both of these two components briefly.
- scenario of program
- Pre-line and post-line

SFT Example for the if-else statement
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a,b,c; cout<<"enter the three numbers"<<endl; cin>>a>>b>>c; if(a>b && a>c) cout<<a<<" is Greater than : "<<b<<" and "<<c; else if (b>a && b>c) cout<<b<<" is Greater than : "<<a<<" and "<<c; else cout<<c<<" is Greater than : "<<b<<" and "<<a; } |

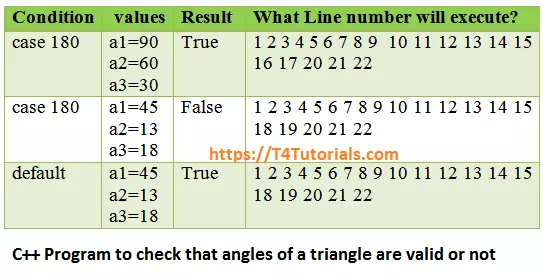
SFT Example for the switch statement
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a1,a2,a3,add; cout<<"enter angle1 of triangle "; cin>>a1; cout<<"enter angle2 of triangle"; cin>>a2; cout<<"enter angle3 of triangle"; cin>>a3; add=a1+a2+a3; switch (add) { case 180: cout<<"triangle is valid"; break; default: cout<<"triangle is not valid"; } return 0; } |
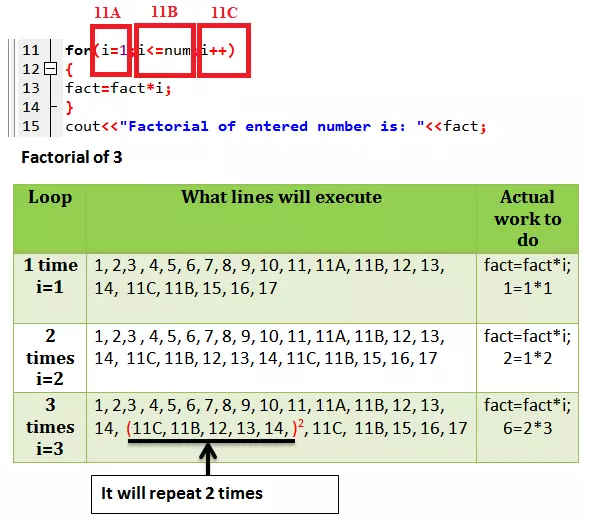
SFT Example for the for loop
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
#include<iostream> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { int i; int num; unsigned long long fact=1; cout<<"Please enter a number: "; cin>>num; for(i=1;i<=num;i++) { fact=fact*i; } cout<<"Factorial of entered number is: "<<fact; getch(); } |
Examples of SFT
- SFT Examples of programs with if-else statements
- SFT Examples of programs with Switch statements
- SFT Examples of programs with Loop