Let’s try to find first and follow for given CFG with the help of a C program.
Output
E=XY X=ilove Y=t4tutorials
C Program To Find First And Follow In Compiler Design
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 |
// C program to calculate the First and // CFG_Follow sets of a given grammar #include<stdio.h> #include<ctype.h> #include<string.h> // Functions to calculate CFG_Follow void T4Tutorials(char, int, int); void CFG_Follow(char c); // Function to calculate First void Searching_First(char, int, int); int count, n = 0; // Stores the final result of the First Sets char FirstCalculation[10][100]; // Stores the final result of the CFG_Follow Sets char calc_CFG_Follow[10][100]; int m = 0; // Stores the production rules char production[10][10]; char f[10], first[10]; int k; char ck; int e; int main(int argc, char **argv) { int jm = 0; int km = 0; int i, choice; char c, ch; count = 4; // The Input grammar strcpy(production[0], "E=XY"); strcpy(production[1], "X=ilove"); strcpy(production[3], "Y=t4tutorials"); int kay; char done[count]; int ptr = -1; // Initializing the FirstCalculation array for(k = 0; k < count; k++) { for(kay = 0; kay < 100; kay++) { FirstCalculation[k][kay] = '!'; } } int point1 = 0, point2, xxx; for(k = 0; k < count; k++) { c = production[k][0]; point2 = 0; xxx = 0; // Checking if First of c has already been calculated for(kay = 0; kay <= ptr; kay++) if(c == done[kay]) xxx = 1; if (xxx == 1) continue; // Function call Searching_First(c, 0, 0); ptr += 1; // Adding c to the calculated list done[ptr] = c; printf("\n First(%c) = { ", c); FirstCalculation[point1][point2++] = c; // Printing the First Sets of the grammar for(i = 0 + jm; i < n; i++) { int lark = 0, chk = 0; for(lark = 0; lark < point2; lark++) { if (first[i] == FirstCalculation[point1][lark]) { chk = 1; break; } } if(chk == 0) { printf("%c, ", first[i]); FirstCalculation[point1][point2++] = first[i]; } } printf("}\n"); jm = n; point1++; } printf("\n"); printf("****************************************\n\n\n"); char donee[count]; ptr = -1; // Initializing the calc_CFG_Follow array for(k = 0; k < count; k++) { for(kay = 0; kay < 100; kay++) { calc_CFG_Follow[k][kay] = '!'; } } point1 = 0; int land = 0; for(e = 0; e < count; e++) { ck = production[e][0]; point2 = 0; xxx = 0; // Checking if CFG_Follow of ck // has alredy been calculated for(kay = 0; kay <= ptr; kay++) if(ck == donee[kay]) xxx = 1; if (xxx == 1) continue; land += 1; // Function call CFG_Follow(ck); ptr += 1; // Adding ck to the calculated list donee[ptr] = ck; printf(" CFG_Follow(%c) = { ", ck); calc_CFG_Follow[point1][point2++] = ck; // Printing the CFG_Follow Sets of the grammar for(i = 0 + km; i < m; i++) { int lark = 0, chk = 0; for(lark = 0; lark < point2; lark++) { if (f[i] == calc_CFG_Follow[point1][lark]) { chk = 1; break; } } if(chk == 0) { printf("%c, ", f[i]); calc_CFG_Follow[point1][point2++] = f[i]; } } printf(" }\n\n"); km = m; point1++; } } void CFG_Follow(char c) { int i, j; // Adding "$" to the CFG_Follow, set of the start symbol if(production[0][0] == c) { f[m++] = '$'; } for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for(j = 2;j < 10; j++) { if(production[i][j] == c) { if(production[i][j+1] != '\0') { // Calculate the first of the next // Variable (Non-Terminal ) in the production T4Tutorials(production[i][j+1], i, (j+2)); } if(production[i][j+1]=='\0' && c!=production[i][0]) { // Calculate the CFG_Follow of the Variable (Non-Terminal ) // in the L.H.S. of the production CFG_Follow(production[i][0]); } } } } } void Searching_First(char c, int q1, int q2) { int j; // The case where we // encounter a Terminal if(!(isupper(c))) { first[n++] = c; } for(j = 0; j < count; j++) { if(production[j][0] == c) { if(production[j][2] == '#') { if(production[q1][q2] == '\0') first[n++] = '#'; else if(production[q1][q2] != '\0' && (q1 != 0 || q2 != 0)) { // Recursion to calculate First of New // Variable (Non-Terminal ) we encounter after epsilon Searching_First(production[q1][q2], q1, (q2+1)); } else first[n++] = '#'; } else if(!isupper(production[j][2])) { first[n++] = production[j][2]; } else { // Recursion to calculate First of // New Variable (Non-Terminal ) we encounter // at the beginning Searching_First(production[j][2], j, 3); } } } } void T4Tutorials(char c, int c1, int c2) { int k; // The case where we encounter // a Terminal if(!(isupper(c))) f[m++] = c; else { int i = 0, j = 1; for(i = 0; i < count; i++) { if(FirstCalculation[i][0] == c) break; } //Including the First set of the // Variable (Non-Terminal ) in the CFG_Follow of // the original query while(FirstCalculation[i][j] != '!') { if(FirstCalculation[i][j] != '#') { f[m++] = FirstCalculation[i][j]; } else { if(production[c1][c2] == '\0') { // Case where we reach the // end of a production CFG_Follow(production[c1][0]); } else { // Recursion to the next symbol in case we encounter a "#" T4Tutorials(production[c1][c2], c1, c2+1); } } j++; } } } |
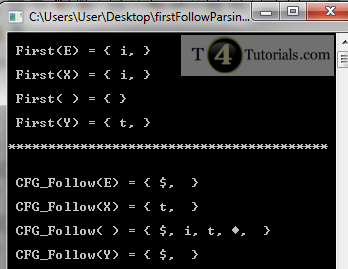
C Code of First and Follow in Parsing[Download]
Rules of First and Follow
A tutorial with easy examples of Rules of First and Follow can be read here.
Compiler Construction Lab Programs in C++
- Lexical analyzer in C++
- Bottom-Up Parsing in C++
- First And Follow in C++
- Parse a string using Operator Precedence parsing in C++