How to Represent Graph with adjacency matrix and adjacency List
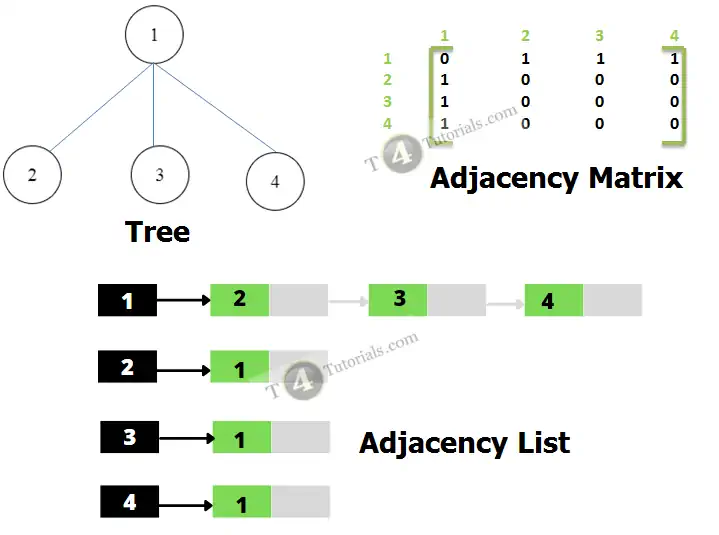
Adjacency Matrix
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int vertexArray[20][20]; //the adjacency matrix initially 0 int count = 0; void showMatrix(int v) { int i, j; for(i = 0; i < v; i++) { for(j = 0; j < v; j++) { cout << vertexArray[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } } void set_edge(int u, int v) { //function to add edge into the matrix vertexArray[u][v] = 1; vertexArray[v][u] = 1; } main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int v = 6; //there are 6 vertices in the graph set_edge(0, 1); set_edge(0, 2); set_edge(0, 3); set_edge(1, 1); set_edge(1, 2); set_edge(1, 3); set_edge(2, 4); set_edge(5, 1); set_edge(5, 2); showMatrix(v); } |
complexity of Adjacency Matrix
The complexity of Adjacency Matrix is O(V2).
Adjacency List
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
#include<iostream> #include<list> #include<iterator> using namespace std; void ShowAdjacencylist(list<int> adj_list[], int v) { for
(int i = 0; i<v; i++) { cout << i << "->"; list<int> :: iterator it; for(it = adj_list[i].begin(); it != adj_list[i].end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } } void setEdge(list<int> adj_list[], int u, int v) { //add v into the list u, and u into list v adj_list[u].push_back(v); adj_list[v].push_back(u); } main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int v = 6; //there are 6 vertices in the graph //create an array of lists whose size is 6 list<int> adj_list[v]; setEdge(adj_list, 0, 1); setEdge(adj_list, 0, 2); setEdge(adj_list, 0, 3); setEdge(adj_list, 1, 2); setEdge(adj_list, 1, 1); setEdge(
adj_list, 2, 4); setEdge(adj_list, 3, 2); setEdge(adj_list, 4, 5); setEdge(adj_list, 5, 1); ShowAdjacencylist(adj_list, v); } |