C++ program to find the volume of a cube, cylinder, and sphere by function overloading.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
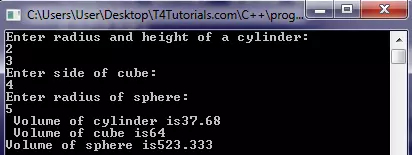
#include<iostream> using namespace std; float T4Tutorials_Volume(int,int); float T4Tutorials_Volume(float); int T4Tutorials_Volume(int); int main() { int r,h,a; float r1; cout<<"Enter radius and height of a cylinder:"<<endl; cin>>r>>h; cout<<"Enter side of cube:"<<endl; cin>>a; cout<<"Enter radius of sphere:"<<endl; cin>>r1; cout<<" Volume of cylinder is"<<T4Tutorials_Volume(r,h)<<endl; cout<<" Volume of cube is"<<T4Tutorials_Volume(a)<<endl; cout<<"Volume of sphere is"<<T4Tutorials_Volume(r1)<<endl; return 0; } float T4Tutorials_Volume(int r,int h) { return(3.14*r*r*h); } float T4Tutorials_Volume(float r1) { return((4*3.14*r1*r1*r1)/3); } int T4Tutorials_Volume(int a) { return(a*a*a); } |
Output
C++ program to find the volume of a sphere
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
#include<iostream> using namespace std; float T4Tutorials_Volume(float); int main() { float r1; cout<<"Enter radius of sphere:"<<endl; cin>>r1; cout<<"Volume of sphere is"<<T4Tutorials_Volume(r1)<<endl; return 0; }
float T4Tutorials_Volume(float r1) { return((4*3.14*r1*r1*r1)/3); } |