[OBJECTIVE]
Subject: Basic Financial Accounting
Time Allowed: 15 Minutes
Max Marks: 10
NOTE: Attempt this Paper on this Question Sheet only. Please encircle the correct option. Division of marks is given in front of each question. This Paper will be collected back after expiry of time limit mentioned above.
Part-I Encircle the right answer, cutting and overwriting are not allowed. (10)
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) Assets — Capital = Liabilities b) Liabilities + Assets = Capital
¢) Liabilities + Capital = Assets d) Assets — Liabilities = Capital
Which of the following is not an asset?
a) Buildings b) Cash balance
c) Accounts receivable d) Loan from HBL
Which of the following is correct?
a) Profit reduces capital b) Profit increases capital
c) Profit does not alter capital d) Capital can only come from profit
Which of the following best describes a trial balance?
a) It shows the financial position of a business b) It is a special account
c) It is a list of balances on the books d) It shows all the entries in the books
Which if the following best describes the meaning of ‘Purchases’?
a) Items bought b) Goods bought on credit
c) Goods bought for resale d) Goods paid for
Suppliers’ personal accounts are found in the:
a) Nominal ledger b) General ledger
c) Purchases ledger d) Sales ledger
7. Which of the following best describes non-current assets?
a) Items bought to be used in the business b) Items which will not wear out quickly
c) Expensive items bought for the business d) Items having a long life and not bought specifically for resale
8. Gross profit is:
a) Excess of sales over cost of goods sold b) Sales less purchases
c) Cost of goods sold + opening inventory d) Net profit less expenses of the period
Capital expenditure is:
a) The extra capital paid in by the proprietor b) The costs of running the business on a day-to-day basis
¢) Money spent on buying non-current assets or adding value to them
d) Money spent on selling non-current assets
An unearned income is an example of:
a) Liability b) Expense
c) Revenue d) Asset
[SUBJECTIVE]
Subject: Financial Accounting (Basic)
Time Allowed: 2 Hours 45 Minutes
Max Marks: 50
NOTE: ATTEMPT THIS (SUBJECTIVE) ON SEPARATE ANSWER SHEET PROVIDED
Part-II Give Short Answers, Each question carries equal marks. (20)
Q#1: Define Depletion.
Q#2: What is Matching Concept?
Q#3: Differentiate between an Unearned Revenue and a Revenue Receivable.
Q#4: Define Current Assets.
Q#5: Differentiate between Returns Inwards and Returns Outwards.
Q#6: What is Statement of Cash Flows? ,
Q#7: What is meant by Acid Test Ratio?
Q#8: What is Straight Line Method of Depreciation?
Q#9: What is the difference between a Sales Ledger and a Purchases Ledger?
Q#10: What is meant by Historical Cost Concept?
Part-III Give Short Answers, Each question carries equal marks. (30)
Q#3: Selected financial data for MMF, s retail store, appear as follows:
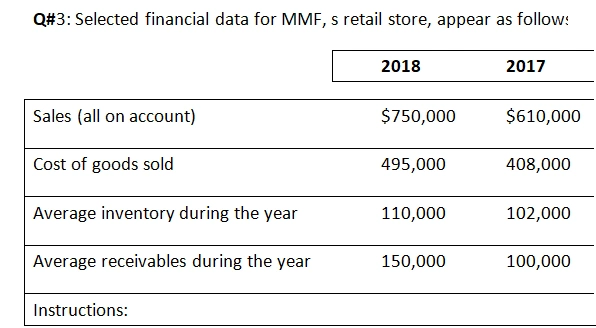
Compute the following for both years:
- Gross Profit percentage
- 2. Inventory turnover
- Accounts receivable turnover
Q#4: JY Internet Consulting Service, Inc., adjusts its accounts every month. Fallowing is the unadjusted trial balance dated December 31, 2018. (Bear in mind that adjusting entries already have been made for the first eleven months of 2018, but nor for December.)
J¥ Internet Consulting Service, Inc. Unadjusted Trial Balance December 31, 2018
Cash $49,100
Consulting fees receivable 23,400
Prepaid office rent 6,300
Prepaid dues and subscriptions 300
Supplies 600
Equipment 36,000
Accumulated depreciation: equipment $10,200
Notes payable 5,000
Income taxes payable 12,000
Unearned consulting fees 5,950
Capital stock 30,000
Retained earnings 32,700
Dividends 60,000
Consulting fees earned 257,180
Salaries expense 88,820
Telephone expense 2,550
Rent expense 22,000
Income taxes expense $1,000
Dues and subscriptions expense 560
Supplies expense 1,600
Depreciation expense: equipment 6,600
Miscellaneous expenses 4,200
$355,030 $353,050
Other Data:
- On December 01, the company signed a new rental agreement and paid three months’ rent in advance at a rate of $2,100 per month. This advance payment was debited to the Prepaid Office Rent account. 1:
- Dues and subscriptions expiring during December amounted to $50. :
- An estimate of supplies on hand was made at December 31; the estimated cost of the unused supplies was $450.
- The useful life of the equipment has been estimated at five years (60 months) from date of acquisition.
- e. Accrued interest on notes payable amounted to $100 at year-end. (Set up accounts for Interest Expense and for Interest Payable.)
- Consulting services valued at $2,850 were rendered during December to clients who had made payment in advance.
- It is the custom of the firm to bill clients only when consulting work is completed or, in the case of prolonged engagements, at monthly intervals. At December 31, consulting services valued at $11,000 had been rendered to clients but not yet billed. No advance payments had been received from these clients.
- Salaries earned by employees but not paid as of December 31 amount to $1,700.
- Income taxes expense for the year is estimated at $56,000. Of this amount, $51,000 has been recognized as expense in prior months, and $39,000 has been paid to tax authorities. The company plans to pay the $17,000 remainder of its income tax liability on January 15.
Instructions:
- Prepare the necessary adjusting journal entries on December 31, 2018.
- Prepare an income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 after making above adjustments.
Q#5: Glenn Grimes is the founder and president of Heartland Construction, a real estate development venture. The business transactions during February while the company was being organized are listed below:
Feb. 01 Grimes and several others invested $500,000 cash in the business in exchange for 25,000 shares of capital stock.
Feb. 10 The company purchased office facilities for $300,000, of which $100,000 was applicable to the land, and $200,000 to the building. A cash payment of $60,000 was made and a note payable was issued for the balance of the purchase price.
Feb. 16 Computer equipment was purchased from PC World for $12,000 cash.
Feb. 18 Office furnishings were purchased from Hi-Way Furnishings at a cost of $9,000. A $1,000 cash payment was made at the time of purchase, and an agreement was made to pay the remaining balance in two equal installments due on March 01 and April 01. Hi-Way Furnishings did not require that Heartland signs 3 promissory note.
Feb. 22 Office supplies were purchased from Office World for $300 cash.
Feb. 23 Heartland discovered that it paid too much for a computer printer purchased on Feb. 16. The unit should have cost only $359, but Heartland was charged $395. PC World promised to refund the difference within seven days.
Feb. 27 Mailed Hi-Way Furnishings the first installment due on the account payable for office furnishings purchased on Feb. 18.
Feb, 28 Received $36 from PC World in full settlement of the account receivable created on Feb. 23.
Instructions:
Record each of the above transactions in general journal form. Select the appropriate account titles from the following chart of accounts:
Cash Capital Stock
Accounts Receivable Computer Systems
Office Supplies Notes Payable
Office Furnishings Land
Accounts Payable Office Building