Rules of Operator Overloading in C++
Operator overloading is a type of static or compile-time polymorphism. C++ supports the compile-time polymorphism. The function overloading and the operator overloading are common examples of compile-time polymorphism.
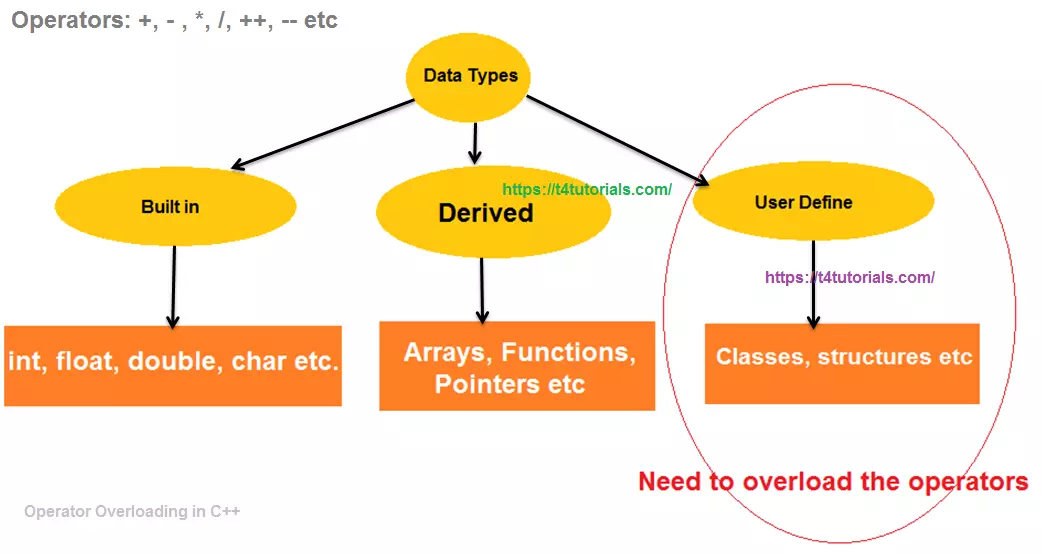
Let’s see the rules for the operator overloading.
- Only built-in operators like (+, -, *, /, etc)can be overloaded.
- We cannot overload all of those operators that are not a part of C++ language like ‘$’.
- We can’t change the arity of the operators. The arity of an operator is the number of operands that the operator takes.
- We can overload the unary operator as an only unary operator, and we cannot overload it as a binary operator and similarly, We can overload binary operators as an only binary operator, and we cannot overload it as a unary operator.
- During the operator overloading, we cannot change the actual meaning of an operator. For example, We cannot overload the plus(+) operator to subtract one value form the other value.
- The precedence of the operators remains the same during operator overloading.
- The operator overloading is not possible for built-in data types. At least one user-defined data types must be there.
- Some operators like assignment “=”, address “&” and comma “,” are by default overloaded.
- When using binary operators overloaded through a member function, the left-hand operand must be an object of the relevant class.
List of operators that can be overloaded
List of operators that can be overloaded are mentioned below;
| + | – | * | / | % | ^ |
| |= | *= | <<= | >>= | [] | () |
| delete | delete [] | new | new [] | -> | ->* |
| << | >> | == | != | && | || |
| += | -= | /= | %= | ^= | &= |
| & | | | ~ | ! | , | = |
| < | > | <= | >= | ++ | — |
More Operator Overloading Programs
- == Operator Overloading in C++.
- insertion and extraction Operator Overloading in C++.
- >= Operator Overloading in C++
- <= Operator Overloading in C++
- program of Logical Or operator Overloading C++.
- Overloading the multiple operators together in a C++program
List of operators that cannot be overloaded
List of operators that cannot be overloaded are mentioned below;
- Scope Resolution Operator (::)
- Pointer-to-member Operator (.*)
- Member Access or Dot operator (.)
- Ternary or Conditional Operator (?:)
- Object size Operator (sizeof)
- Object type Operator (typeid)
How Operator Overloading works with functions in C++
Operator overloading can be done by implementing a function and the function can be a;
- Member Function
- Non-Member Function
- Friend Function
The Member Function and Non-Member Function: Operator overloaded function can be a member function of class X if the Left operand is an object of that class X, but if the Left operand is different, then Operator overloading function must be a non-member function.
The Friend Function: Operator overloaded function can be made friend function of class X if it needs access to the private and protected members of class X.
Operator overloading Examples in C++ [with error]
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class T4Tutorials{
int T4Tutorials_Number;
public:
T4Tutorials()
//constructor
{
T4Tutorials_Number=0;
}
void operator++()
};
int main()
{
T4Tutorials t1;
//t1 is object of class
++t1;
// prefix increment of object
}
Output
[Error] no match for ‘operator++’ (operand type is ‘T4Tutorials’)
Operator overloading Examples in C++ [correct = without error]
This program is showing the operator overloading of the prefix increment operator.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class T4Tutorials{
int T4Tutorials_Number;
public:
T4Tutorials()
//constructor
{
T4Tutorials_Number=0;
}
void operator++()
//function for operator overloading
{
++T4Tutorials_Number;
//prefix increment
cout<<"The operator is overloaded successfully: "<<T4Tutorials_Number<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
T4Tutorials t1;
//t1 is object of class
++t1;
// prefix increment of object
}
Output
The operator is overloaded successfully: 1
Operator overloading of Postfix increment operator in C++
This program is showing the operator overloading of the postfix increment operator.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class T4Tutorials{
int T4Tutorials_Number;
public:
T4Tutorials()
//constructor
{
T4Tutorials_Number=0;
}
void operator++(int)
//function for operator overloading
{
T4Tutorials_Number++;
//prefix increment
cout<<"The operator is overloaded successfully: "<<T4Tutorials_Number<<endl; }
};
int main()
{
T4Tutorials t1;
//t1 is object of class
t1++;
// prefix increment of object
}
Output
The operator is overloaded successfully: 1
Operator overloading of Postfix decrement operator in C++
This program is showing the operator overloading of the postfix decrement operator.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class T4Tutorials{
int T4Tutorials_Number;
public:
T4Tutorials()
//constructor
{
T4Tutorials_Number=0;
}
void operator--(int)
//function for operator overloading
{
T4Tutorials_Number--;
//prefix increment
cout<<"The operator is overloaded successfully: "<<T4Tutorials_Number<<endl; }
};
int main()
{
T4Tutorials t1;
//t1 is object of class
t1--;
// prefix increment of object
}
Output
The operator is overloaded successfully: -1