Summary:
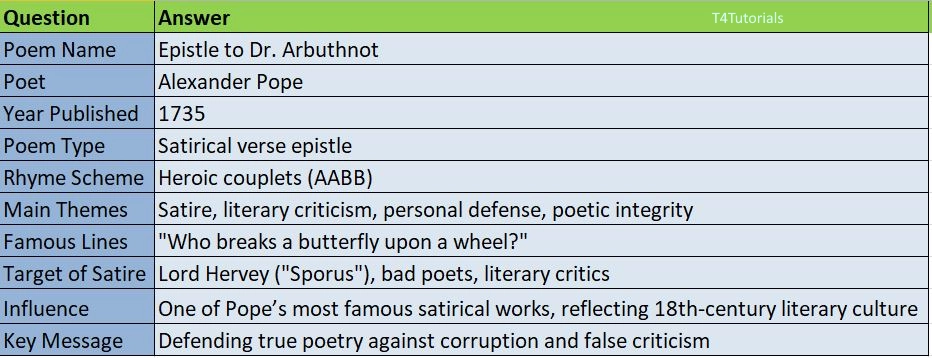
Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot by Alexander Pope is a satirical and autobiographical poem written in the form of a verse letter to his friend, Dr. John Arbuthnot. The poem serves as both a defense of Pope’s literary career and a scathing critique of his enemies, including contemporary poets and critics. It reflects on his struggles as a writer, the attacks he faced from jealous rivals, and his commitment to honesty and poetic integrity. One of the most famous sections includes the attack on Lord Hervey, whom Pope mockingly calls “Sporus.” The poem, written in heroic couplets, is a mix of wit, self-reflection, and sharp satire, solidifying Pope’s reputation as one of the greatest satirists in English literature.
1. : Who is the poet of Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot?
(A) John Dryden
(B) Jonathan Swift
(C) Alexander Pope
(D) Samuel Johnson
2. : In what form is Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot written?
(A) Blank verse
(B) Heroic couplets
(C) Free verse
(D) Ottava rima
3. : What is the primary theme of the poem?
(A) Romantic love
(B) Political rebellion
(C) Defense of Pope’s literary career and satire of his critics
(D) The beauty of nature
4. : Who is the “Sporus” mentioned in the poem?
(A) Jonathan Swift
(B) Lord Hervey
(C) John Arbuthnot
(D) Colley Cibber
5. : What is the tone of the poem?
(A) Lighthearted and humorous
(B) Solemn and tragic
(C) Satirical and defensive
(D) Melancholic and nostalgic
6. : Why did Pope write Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot?
(A) To praise his contemporaries
(B) To attack political figures
(C) To defend his literary career against critics and rivals
(D) To describe his love for nature
7. : Who was Dr. John Arbuthnot?
(A) A literary critic
(B) A physician and satirist
(C) A political leader
(D) A playwright
8. : What poetic device is commonly used in the poem?
(A) Hyperbole
(B) Simile
(C) Satire
(D) Personification
9. : What does Pope criticize in the poem?
(A) Religious leaders
(B) Corrupt poets and critics
(C) The monarchy
(D) The natural world
10. : What literary period does Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot belong to?
(A) Romanticism
(B) Neoclassicism
(C) Modernism
(D) Victorian Era